CUB and Sushi Multiple Domains (CSMD1) Gene Polymorphisms and Susceptibilities to Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease in Northern Chinese Han Population: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 33628416
- PMCID: PMC7896860
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6661162
CUB and Sushi Multiple Domains (CSMD1) Gene Polymorphisms and Susceptibilities to Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease in Northern Chinese Han Population: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
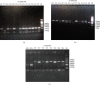
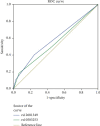
Evidence has shown that the CUB and Sushi Multiple Domains (CSMD1) gene is an inhibitor of the complement activation pathway and is also involved in central nervous system inflammation. Previous studies have revealed that the CSMD1 gene is related to familial Parkinson's disease. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between CSMD1 gene and susceptibility to Parkinson's disease in population of northern China. A case-control study was performed on 423 Parkinson's disease patients and 465 healthy controls matched for age and sex. DNA from enrolled subjects were extracted from the peripheral blood, and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs12681349 (C>T), rs10503253 (C>A), and rs1983474 (T>G) within CSMD1 gene were genotyped using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). Genotype frequency of rs10503253 (CA versus CC : OR = 1.554, 95% CI = 1.169-2.066, p=0.002) and rs1983474 (GG versus TT : OR = 0.599, 95% CI = 0.401-0.895, p=0.012) was significantly different between PD cases and controls, but not for rs12681349. Comprehensive and subgroup analysis indicated that rs10503252 showed significant statistical differences in the dominant model (AA + CA versus CC : OR = 0.677, 95% CI = 0.517-0.886, p=0.004), late-onset cohort (CA versus CC : OR = 1.570, 95% CI = 1.159-2.126, p=0.004), and the female cohort (CA versus CC : OR = 0.687, 95% CI = 0.497-0.952, p=0.023), compared with the matched control group. The difference of recessive model of rs1983474 (GG versus TT + TG : OR = 1.837, 95% CI = 1.287-2.620, p=0.001) was significant in Parkinson's disease. According to the subgroup analysis, results indicated that late-onset cohort (GG versus TT : OR = 0.643, 95% CI = 0.420-0.985, p=0.042), male cohort (TG versus TT : OR = 2.160, 95% CI = 1.162-4.016, p=0.015), and female group (GG versus TT : OR = 0.418, 95% CI = 0.234-0.746, p=0.003) of rs1983474 were significantly associated with Parkinson's disease susceptibility. In both genotype and subgroup analysis, we failed to find any relationship between rs12681349 polymorphism and Parkinson's disease risk. Our results indicate that the rs10503253 and rs1983474 gene polymorphism may be associated with idiopathic Parkinson's disease susceptibility in Chinese population. Nevertheless, these conclusions need to be further verified by more studies.
Copyright © 2021 Xinling Bai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

