Haematococcus pluvialis Carotenoids Enrich Fractions Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis Induced by Thioacetamide in Rats: Modulation of Metalloproteinase and Its Inhibitor
- PMID: 33628797
- PMCID: PMC7895575
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6631415
Haematococcus pluvialis Carotenoids Enrich Fractions Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis Induced by Thioacetamide in Rats: Modulation of Metalloproteinase and Its Inhibitor
Abstract
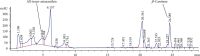
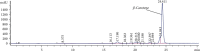
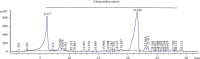
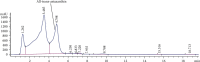
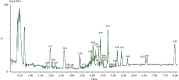
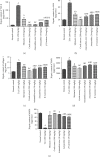
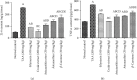
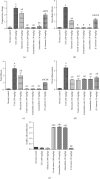
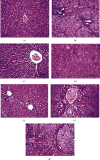
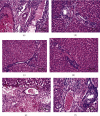
Hepatic fibrosis is a consequence of chronic liver diseases. Metalloproteinase and its inhibitor have crucial roles in the resolution of liver fibrosis. The current relevant study is aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect of Haematococcus pluvialis (H. pluvialis) extract, astaxanthin-rich fraction, astaxanthin ester-rich fraction, and β-carotene-rich fraction as well as their mechanisms of action in curing hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide (TAA). Liver fibrosis was induced using TAA (intraperitoneal injection, two times a week for 6 weeks), in a rat model and H. pluvialis extract (200 mg/kg), and other fractions (30 mg/kg) were orally administered daily for 4 weeks after the last TAA injection. Based on HPLC analysis, H. pluvialis extract contains β-carotene (12.95 mg/g, extract) and free astaxanthin (10.85 mg/g, extract), while HPLC/ESI-MS analysis revealed that H. pluvialis extract contains 28 carotenoid compounds including three isomers of free astaxanthin, α or β-carotene, lutein, 14 astaxanthin mono-esters, 5 astaxanthin di-esters, and other carotenoids. H. pluvialis and its fractions reduced liver enzymes, nitric oxide, collagen 1, alpha-smooth muscle actin, and transforming growth factor-beta as well as elevated catalase antioxidant activity compared to the TAA group. Also, H. pluvialis extract and its fractions exceedingly controlled the balance between metalloproteinase and its inhibitor, activated Kupffer cells proliferation, and suppressed liver apoptosis, necrobiosis, and fibrosis. These findings conclude that H. pluvialis extract and its fractions have an antifibrotic effect against TAA-induced liver fibrosis by regulating the oxidative stress and proinflammatory mediators, suppressing multiple profibrogenic factors, and modulating the metalloproteinase and its inhibitor pathway, recommending H. pluvialis extract and its fractions for the development of new effective medicine for treating hepatic fibrosis disorders.
Copyright © 2021 Farouk K. El-Baz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of pomegranate extract and curcumin ameliorates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats: impact on TGF-β/Smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2020 Oct;30(8):620-633. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2020.1801926. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2020. PMID: 32718261
-
Estrogen Deficiency Potentiates Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 29;20(15):3709. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153709. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31362375 Free PMC article.
-
Maltol Mitigates Thioacetamide-induced Liver Fibrosis through TGF-β1-mediated Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Feb 6;67(5):1392-1401. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05943. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30644744
-
Comparative assessment on the extraction of carotenoids from microalgal sources: Astaxanthin from H. pluvialis and β-carotene from D. salina.Food Chem. 2019 Mar 30;277:128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.066. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30502128 Review.
-
Haematococcus pluvialis as a Potential Source of Astaxanthin with Diverse Applications in Industrial Sectors: Current Research and Future Directions.Molecules. 2021 Oct 27;26(21):6470. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216470. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant effects of astaxanthin and metformin combined therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial.Res Pharm Sci. 2022 Jan 15;17(2):219-230. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.335179. eCollection 2022 Apr. Res Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35280834 Free PMC article.
-
Can Nutraceuticals Support the Treatment of MASLD/MASH, and thus Affect the Process of Liver Fibrosis?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 11;25(10):5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105238. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of green tea against Thioacetamide-Induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rats.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan;29(1):564-573. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.023. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002452 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant activity and protective effect of phyto-active compounds of Crataegus azarolus berries decoction extract against acetic acid-induced hepatorenal injuries in male rats.Physiol Rep. 2025 Feb;13(3):e70240. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70240. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39924696 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Saccharomyces Cervisciae Cell Wall Extract against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats.Heliyon. 2021 May 27;7(6):e07159. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07159. eCollection 2021 Jun. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34159266 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

