Serum IL-37 Level Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Disease Activity: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33628802
- PMCID: PMC7884130
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6653439
Serum IL-37 Level Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Disease Activity: A Meta-Analysis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Serum IL-37 Level Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Disease Activity: A Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9827814. doi: 10.1155/2023/9827814. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38075348 Free PMC article.
Abstract
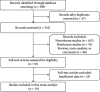
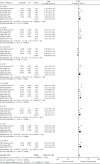
Interleukin-37 (IL-37) inhibits the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) via downregulating proinflammatory cytokines. Accordingly, we performed an analysis to accurately assess the relationship between serum IL-37 cytokine levels and disease activity of RA. Subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were applied to explore the sources of heterogeneity. Correlation coefficient (r) was utilized to evaluate the relationship between IL-37 and disease activity of RA patients. Ten studies were included into the research. Functional analysis revealed elevated serum IL-37 concentrations in RA patients (SMD = 1.61, P < 0.00001). The relationship between serum IL-37 levels and disease activity was statistically significant (C-reactive protein: r = 1.47, P = 0.0002; erythrocyte sedimentation rate: r = 1.55, P < 0.00001; rheumatoid factor: r = 1.40, P = 0.004; tumor necrosis factor⁃α: r = 1.64, P = 0.0003; Disease Activity Score for 28 joints: r = 1.63, P < 0.00001; tender joint count: r = 1.48, P < 0.00001; and swollen joint count: r = 1.52, P = 0.0003), but anti-CCP was not significant (anti-CCP: r = 0.98, P = 0.72). In summary, these data are suggesting that the elevated serum level of IL-37 in RA is positively correlated with the disease activity of RA, suggesting a role for IL-37in the pathogenesis of RA.
Copyright © 2021 Shengnan Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

