Ultrasound May Suppress Tumor Growth, Inhibit Inflammation, and Establish Tolerogenesis by Remodeling Innatome via Pathways of ROS, Immune Checkpoints, Cytokines, and Trained Immunity/Tolerance
- PMID: 33628851
- PMCID: PMC7889351
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6664453
Ultrasound May Suppress Tumor Growth, Inhibit Inflammation, and Establish Tolerogenesis by Remodeling Innatome via Pathways of ROS, Immune Checkpoints, Cytokines, and Trained Immunity/Tolerance
Abstract
Background: The immune mechanisms underlying low-intensity ultrasound- (LIUS-) mediated suppression of inflammation and tumorigenesis remain poorly determined.
Methods: We used microarray datasets from the NCBI GEO DataSet repository and conducted comprehensive data-mining analyses, where we examined the gene expression of 1376 innate immune regulators (innatome genes (IGs) in cells treated with LIUS.
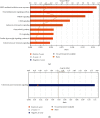
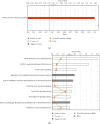
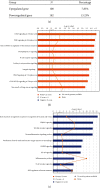
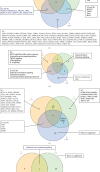
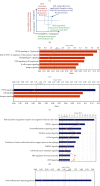
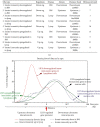
Results: We made the following findings: (1) LIUS upregulates proinflammatory IGs and downregulates metastasis genes in cancer cells, and LIUS upregulates adaptive immunity pathways but inhibits danger-sensing and inflammation pathways and promote tolerogenic differentiation in bone marrow (BM) cells. (2) LIUS upregulates IGs encoded for proteins localized in the cytoplasm, extracellular space, and others, but downregulates IG proteins localized in nuclear and plasma membranes, and LIUS downregulates phosphatases. (3) LIUS-modulated IGs act partially via several important pathways of reactive oxygen species (ROS), reverse signaling of immune checkpoint receptors B7-H4 and BTNL2, inflammatory cytokines, and static or oscillatory shear stress and heat generation, among which ROS is a dominant mechanism. (4) LIUS upregulates trained immunity enzymes in lymphoma cells and downregulates trained immunity enzymes and presumably establishes trained tolerance in BM cells. (5) LIUS modulates chromatin long-range interactions to differentially regulate IGs expression in cancer cells and noncancer cells.
Conclusions: Our analysis suggests novel molecular mechanisms that are utilized by LIUS to induce tumor suppression and inflammation inhibition. Our findings may lead to development of new treatment protocols for cancers and chronic inflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Qian Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Experimental Data-Mining Analyses Reveal New Roles of Low-Intensity Ultrasound in Differentiating Cell Death Regulatome in Cancer and Non-cancer Cells via Potential Modulation of Chromatin Long-Range Interactions.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 12;9:600. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00600. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31355136 Free PMC article.
-
Low‑intensity ultrasound enhances the antitumor effects of doxorubicin on hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the ROS‑miR‑21‑PTEN axis.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Mar;21(3):989-998. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10936. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32016465 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Intensity Ultrasound Decreases α-Synuclein Aggregation via Attenuation of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in MPP(+)-Treated PC12 Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Oct;54(8):6235-6244. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0104-z. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27714630
-
Progression in low-intensity ultrasound-induced tumor radiosensitization.Cancer Med. 2024 Jul;13(13):e7332. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7332. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38967145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria driven innate immune signaling and inflammation in cancer growth, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2024;386:223-247. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2024.01.006. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38782500 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound affects proliferation and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr 10;151(4):136. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06183-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40208346 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity of vascular smooth muscle cells contributes to two-wave inflammation in atherosclerosis, twin-peak inflammation in aortic aneurysms and trans-differentiation potential into 25 cell types.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 24;14:1348238. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1348238. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38327764 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette Smoke Modulates Inflammation and Immunity via Reactive Oxygen Species-Regulated Trained Immunity and Trained Tolerance Mechanisms.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 May;38(13-15):1041-1069. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0087. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36017612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in mitochondrial-targeted nanotherapeutics: overcoming biological obstacles and optimizing drug delivery.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1451989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451989. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aorta in Pathologies May Function as an Immune Organ by Upregulating Secretomes for Immune and Vascular Cell Activation, Differentiation and Trans-Differentiation-Early Secretomes may Serve as Drivers for Trained Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 7;13:858256. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.858256. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35320939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang Q., Nanayakkara G. K., Drummer C., et al. Low-intensity ultrasound-induced anti-inflammatory effects are mediated by several new mechanisms including gene induction, immunosuppressor cell promotion, and enhancement of exosome biogenesis and docking. Frontiers in Physiology. 2017;8:p. 818. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00818. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

