Proton-Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Community-Associated Clostridium difficile Infection
- PMID: 33629099
- PMCID: PMC8204777
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1857
Proton-Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Community-Associated Clostridium difficile Infection
Abstract
Background: Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) have been reported to increase the risk of community-associated Clostridium difficile infection (CDI), but the association remains disputed.
Methods: A nationwide cohort study among adults in Denmark, 2010-2013, linking register data on C. difficile testing, filled prescriptions, and patient characteristics. All incident episodes of community-associated CDI (ie, positive culture, molecular assay, or toxin test in individuals without previous hospitalization in the prior 12 weeks and without a positive test for C. difficile in the prior 8 weeks) were identified in the Danish National Microbiological Database. Self-controlled case-series analyses were used to estimate incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for community-associated CDI, comparing periods with and without exposure to PPIs. By design, models took fixed confounders such as chronic disease, genetics, and socioeconomic status into account; further, time-varying confounders, including hospital stay and antibiotic and corticosteroid use were adjusted for.
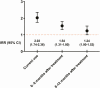
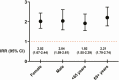
Results: 3583 episodes of community-associated CDI were identified, of which 964 occurred during current use of PPIs, 324 occurred 0-6 months after treatment cessation, 123 occurred 6-12 months after treatment cessation, and 2172 occurred during time periods without use of PPIs. The adjusted IRR was 2.03 (95% confidence interval, 1.74-2.36), comparing use of PPI with nonuse. The increased risk remained elevated in later time periods: 1.54 (1.31-1.80) for 0-6 months, 1.24 (1.00-1.53) for 6-12 months after current use.
Conclusions: Use of PPIs was associated with moderately increased risk of community-associated CDI. The risk remained elevated up to 1 year after PPI treatment had ended.
Keywords: C. difficile infection; epidemiology; proton-pump inhibitor; self-controlled case-series analysis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
Comment in
-
Proton Pump Inhibitors and Incident Clostridioides difficile Infection: Beyond Controversy, Pragmatic Approaches Are Needed.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 15;72(12):e1090-e1092. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1856. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33320187 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Furuya-Kanamori L, Stone JC, Clark J, et al. . Comorbidities, exposure to medications, and the risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2015; 36:132–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

