Kinetics and Mechanisms of Virus Inactivation by Chlorine Dioxide in Water Treatment: A Review
- PMID: 33629148
- PMCID: PMC7904506
- DOI: 10.1007/s00128-021-03137-3
Kinetics and Mechanisms of Virus Inactivation by Chlorine Dioxide in Water Treatment: A Review
Abstract
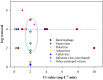
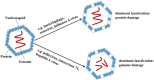
Chlorine dioxide (ClO2), an alternative disinfectant to chlorine, has been widely applied in water and wastewater disinfection. This paper aims at presenting an overview of the inactivation kinetics and mechanisms of ClO2 with viruses. The inactivation efficiencies vary greatly among different virus species. The inactivation rates for different serotypes within a family of viruses can differ by over 284%. Generally, to achieve a 4-log removal, the exposure doses, also being referred to as Ct values (mutiplying the concentration of ClO2 and contact time) vary in the range of 0.06-10 mg L-1 min. Inactivation kinetics of viruses show two phases: an initial rapid inactivation phase followed by a tailing phase. Inactivation rates of viruses increase as pH or temperature increases, but show different trends with increasing concentrations of dissolved organic matter (DOM). Both damages in viral proteins and in the 5' noncoding region within the genome contribute to virus inactivation upon ClO2 disinfection.
Keywords: Chlorine dioxide (ClO2); Disinfection; Kinetics; Mechanisms; Virus; Water treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chlorine dioxide oxidation of Escherichia coli in water - A study of the disinfection kinetics and mechanism.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2017 Jun 7;52(7):598-606. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2017.1293993. Epub 2017 Mar 16. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2017. PMID: 28301286
-
Kinetic and mechanistic understanding of chlorite oxidation during chlorination: Optimization of ClO2 pre-oxidation for disinfection byproduct control.Water Res. 2022 Jul 15;220:118515. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118515. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Water Res. 2022. PMID: 35700645
-
Comparison of chlorine and chlorine dioxide disinfection in drinking water: Evaluation of disinfection byproduct formation under equal disinfection efficiency.Water Res. 2024 Aug 15;260:121932. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2024.121932. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Water Res. 2024. PMID: 38906077
-
Chlorine dioxide-based oxidation processes for water purification:A review.J Hazard Mater. 2022 Aug 15;436:129195. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129195. Epub 2022 May 21. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 35739725
-
Application of chlorine dioxide and its disinfection mechanism.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Sep 10;206(10):400. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04137-7. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39256286 Review.
Cited by
-
Estimation of alkali dosage and contact time for treating human excreta containing viruses as an emergency response: a systematic review.Front Public Health. 2023 Nov 10;11:1286595. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1286595. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38026419 Free PMC article.
-
New Countermeasures Against Infections with/after COVID-19: Is Chlorine Dioxide a Useful and Safe Disinfectant?Juntendo Iji Zasshi. 2022 Oct 15;68(5):465-472. doi: 10.14789/jmj.JMJ22-0030-R. eCollection 2022. Juntendo Iji Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 39081585 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal Mechanisms of Chlorine Dioxide against Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcus CMCC 32210.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jun 13;45(6):5132-5144. doi: 10.3390/cimb45060326. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37367075 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of surface disinfection methods to inactivate the beta coronavirus Murine Hepatitis Virus.J Occup Environ Hyg. 2022 Aug;19(8):455-468. doi: 10.1080/15459624.2022.2088768. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2022. PMID: 35687041 Free PMC article.
-
Disinfectants against SARS-CoV-2: A Review.Viruses. 2022 Aug 4;14(8):1721. doi: 10.3390/v14081721. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AWWA Water Quality Division Committee report: disinfection at large and medium-size systems. J Am Water Work Assoc. 2000;92:32–43. doi: 10.1002/j.1551-8833.2000.tb08942.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

