Evaluation of patient engagement in medicine development: A multi-stakeholder framework with metrics
- PMID: 33629470
- PMCID: PMC8077089
- DOI: 10.1111/hex.13191
Evaluation of patient engagement in medicine development: A multi-stakeholder framework with metrics
Abstract
Background: Patient engagement is becoming more customary in medicine development. However, embedding it in organizational decision-making remains challenging, partly due to lack of agreement on its value and the means to evaluate it. The objective of this project was to develop a monitoring and evaluation framework, with metrics, to demonstrate impact and enhance learning.
Methods: A consortium of five patient groups, 15 biopharmaceutical companies and two academic groups iteratively created a framework in a multi-phase participatory process, including analysis of its application in 24 cases.
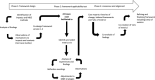
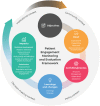
Results: The framework includes six components, with 87 metrics and 15 context factors distributed among (sub)components: (a) Input: expectations, preparations, resources, representativeness of stakeholders; (b) Activities/process: structure, management, interactions, satisfaction; (c) Learnings and changes; (d) Impacts: research relevance, study ethics and inclusiveness, study quality and efficiency, quality of evidence and uptake of products, empowerment, reputation and trust, embedding of patient engagement; (e) Context: policy, institutional, community, decision-making contextual factors. Case study findings show a wide variation in use of metrics. There is no 'one size fits all' set of metrics appropriate for every initiative or organization. Presented sample sets of metrics can be tailored to individual situations.
Conclusion: Introducing change into any process is best done when the value of that change is clear. This framework allows participants to select what metrics they value and assess to what extent patient engagement has contributed.
Patient contribution: Five patient groups were involved in all phases of the study (design, conduct, interpretation of data) and in writing the manuscript.
Keywords: impact; metrics; monitoring and evaluation; patient engagement; patient participation; quality indicators.
© 2021 The Authors. Health Expectations published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monitoring and Evaluation of Patient Engagement in Health Product Research and Development: Co-Creating a Framework for Community Advisory Boards.J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2022 Jan 17;9(1):46-57. doi: 10.17294/2330-0698.1859. eCollection 2022 Winter. J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35111882 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Utilizing patient advocates in Parkinson's disease: A proposed framework for patient engagement and the modern metrics that can determine its success.Health Expect. 2020 Aug;23(4):722-730. doi: 10.1111/hex.13064. Epub 2020 May 3. Health Expect. 2020. PMID: 32363785 Free PMC article.
-
Metrics and Evaluation Tools for Patient Engagement in Healthcare Organization- and System-Level Decision-Making: A Systematic Review.Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Oct 1;7(10):889-903. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2018.43. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 30316241 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring patient engagement with HIV care in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping study.J Int AIDS Soc. 2022 Oct;25(10):e26025. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26025. J Int AIDS Soc. 2022. PMID: 36285618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the impact of engaging older adults and service providers as research partners in the co-design of a community mobility-promoting program: a mixed methods developmental evaluation study.Res Involv Engagem. 2023 Dec 8;9(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s40900-023-00523-5. Res Involv Engagem. 2023. PMID: 38062536 Free PMC article.
-
Embedding patient engagement in the R&D process of a life sciences company through co-creation with a patient expert R&D board: a case study.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Nov 6;10(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00631-w. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 39506875 Free PMC article.
-
Measurable outcomes of consumer engagement in health research: A scoping review.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 17;10:994547. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.994547. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36324444 Free PMC article.
-
Researchers' experiences with patient engagement in health research: a scoping review and thematic synthesis.Res Involv Engagem. 2023 Apr 10;9(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40900-023-00431-8. Res Involv Engagem. 2023. PMID: 37038164 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Impacts of Patient Engagement on Health Services Research Teams: Lessons from the Veteran Consulting Network.J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Apr;37(Suppl 1):33-41. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-06987-z. Epub 2022 Mar 29. J Gen Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35349028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis C, Naci H, Gurpinar E, Poplavska E, Pinto A, Aggarwal A. Availability of evidence of benefits on overall survival and quality of life of cancer drugs approved by European Medicines Agency: retrospective cohort study of drug approvals 2009–13. BMJ. 2017;359:j4530. 10.1136/bmj.j4530 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources