Best practices to ensure robust investigation of circular RNAs: pitfalls and tips
- PMID: 33629517
- PMCID: PMC7926241
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.202052072
Best practices to ensure robust investigation of circular RNAs: pitfalls and tips
Abstract
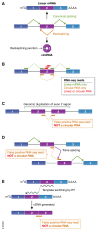
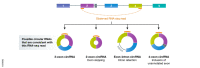
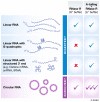
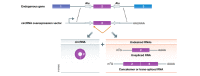
Pre-mRNAs from thousands of eukaryotic genes can be non-canonically spliced to generate circular RNAs (circRNAs) that have covalently linked ends. Most mature circular RNAs are expressed at low levels, but some have known physiological functions and/or accumulate to higher levels than their associated linear mRNAs. These observations have sparked great interest into this class of previously underappreciated RNAs and prompted the development of new experimental approaches to study them, especially methods to measure or modulate circular RNA expression levels. Nonetheless, each of these approaches has caveats and potential pitfalls that must be controlled for when designing experiments and interpreting results. Here, we provide practical advice, tips, and suggested guidelines for performing robust identification, validation, and functional characterization of circular RNAs. Beyond promoting rigor and reproducibility, these suggestions should help bring clarity to the field, especially how circular RNAs function and whether these transcripts may sponge microRNAs/proteins or serve as templates for translation.
Keywords: RNase R; backsplicing; circRNA; microRNA sponge; translation.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL et al (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real‐time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55: 611–622 - PubMed
-
- Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, Goodfellow P, Lovell‐Badge R (1993) Circular transcripts of the testis‐determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 73: 1019–1030 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

