Preoperative consolidation-to-tumor ratio is effective in the prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients with pulmonary ground-glass component nodules
- PMID: 33629518
- PMCID: PMC8046132
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13899
Preoperative consolidation-to-tumor ratio is effective in the prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients with pulmonary ground-glass component nodules
Abstract
Background: Preoperative positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) is recommended as a guideline for staging of lung cancer. However, for patients with pulmonary ground-glass opacity (GGO) nodules who are supposed to have a relatively low risk of incidence of lymphatic metastasis, it remains uncertain whether PET/CT is more effective than consolidation-to-tumor ratio (CTR) in the prediction of regional lymphatic metastasis.
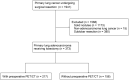
Methods: The data on patients who underwent surgery for lung cancer from 2011 to 2016 were collected retrospectively, which included CTR, results of PET/CT, and pathological characteristics. The patients who had undergone preoperative PET/CT were identified to find the risk factors for lymphatic metastasis. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and multiple logistic regression was utilized to clarify the predictive value of CTR and main tumor maximal standardized uptake value (SUVmax).
Results: Among 217 patients who had PET/CT before lobectomy, chest computed tomography revealed that 75 patients had CTR greater than 62%. The patients with lymphatic metastasis were shown to have higher CTR and higher main tumor SUVmax. Multiple logistic regression showed that younger age (<60 years), higher main tumor SUVmax on PET/CT, and greater CTR were independent predictive factors for lymphatic metastasis. The area under the ROC curve was comparable, 0.817 for CTR, and 0.816 for main tumor SUVmax.
Conclusions: The present study revealed that CTR was not inferior to main tumor SUVmax considering the predictive power for lymphatic metastasis preoperatively in lung cancer patients with a GGO component. PET/CT might not be necessary preoperatively in selected patients.
Keywords: consolidation-to-tumor ratio; ground-glass opacity; lung cancer; positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
© 2021 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare, and there was no funding for this study.
Figures

References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network . Non‐small Cell Lung Cancer (Version 5. 2019). 2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf. accessed date: 16 February 2021
-
- Woodard GA, Jones KD, Jablons DM. Lung cancer staging and prognosis. Cancer Treat Res. 2016;170:47–75. - PubMed
-
- Cerfolio RJ, Ojha B, Bryant AS, Raghuveer V, Mountz JM, Bartolucci AA. The accuracy of integrated PET‐CT compared with dedicated PET alone for the staging of patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78(3):1017–23; discussion −23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

