Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis globally: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33630060
- PMCID: PMC8516513
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab190
Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis globally: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis on the incidence and prevalence of SSc covering the entire literature.
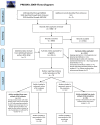
Methods: This study followed the recommendations of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement of 2009. We conducted a systematic search in MEDLINE, Web of Science and Embase to identify articles reporting incidence and/or prevalence of SSc. Two authors conducted the search, reviewed articles for inclusion and extracted relevant data. We used random-effects models to estimate the pooled prevalence and incidence of SSc and performed subgroup analyses by sex, case definition and region to investigate heterogeneity. We explored the association between calendar period and reported estimates using meta-regression.
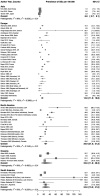
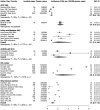
Results: Among 6983 unique records identified, we included 61 studies of prevalence and 39 studies of incidence in the systematic review. The overall pooled prevalence of SSc was 17.6 (95% CI 15.1, 20.5) per 100 000 and the overall pooled incidence rate of SSc was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1, 1.9) per 100 000 person-years. We observed significant regional variations in reported estimates; studies conducted in North America reported considerably higher estimates than other regions. The pooled incidence and prevalence in women were five times higher than in men. More recent studies reported higher estimates than older ones.
Conclusion: In this comprehensive review of the incidence and prevalence of SSc across the world, there was large heterogeneity among estimates, which should be taken into consideration when interpreting the results.
Keywords: incidence; meta-analysis; prevalence; systematic review; systemic sclerosis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- Jimenez SA, Derk CT.. Following the molecular pathways toward an understanding of the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:37–50. - PubMed
-
- Allanore Y, Simms R, Distler O. et al. Systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015;1:15002. - PubMed
-
- Denton CP, Khanna D.. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017;390:1685–99. - PubMed
-
- Hughes M, Pauling JD, Armstrong-James L. et al. Gender-related differences in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 2020;19:102494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

