Roxadustat for the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (ALPS)
- PMID: 33630072
- PMCID: PMC8397511
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfab057
Roxadustat for the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients not on dialysis: a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (ALPS)
Abstract
Background: Roxadustat is an orally active hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD) anemia.
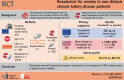
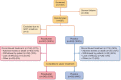
Methods: This Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined patients with Stages 3-5 CKD, not on dialysis (NCT01887600). Patients were randomized (2:1) to oral roxadustat or placebo three times weekly for 52-104 weeks. This study examined two primary efficacy endpoints: European Union (European Medicines Agency)-hemoglobin (Hb) response, defined as Hb ≥11.0 g/dL that increased from baseline (BL) by ≥1.0 g/dL in patients with Hb >8.0 g/dL or ≥2.0 g/dL in patients with BL Hb ≤8.0 g/dL, without rescue therapy, during the first 24 weeks of treatment; US Food and Drug Administration-change in Hb from BL to the average Hb level during Weeks 28-52, regardless of rescue therapy. Secondary efficacy endpoints and safety were examined.
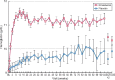
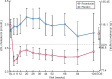
Results: A total of 594 patients were analyzed (roxadustat: 391; placebo: 203). Superiority of roxadustat versus placebo was demonstrated for both primary efficacy endpoints: Hb response [odds ratio = 34.74, 95% confidence interval (CI) 20.48-58.93] and change in Hb from BL [roxadustat - placebo: +1.692 (95% CI 1.52-1.86); both P < 0.001]. Superiority of roxadustat was demonstrated for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol change from BL, and time to first use of rescue medication (both P < 0.001). The incidences of treatment-emergent adverse events were comparable between groups (roxadustat: 87.7%, placebo: 86.7%).
Conclusions: Roxadustat demonstrated superior efficacy versus placebo in terms of both Hb response rate and change in Hb from BL. The safety profiles of roxadustat and placebo were comparable.
Keywords: anemia; chronic kidney disease; iron; non-dialysis; roxadustat.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures

References
-
- Shih HM, Wu CJ, Lin SL.. Physiology and pathophysiology of renal erythropoietin-producing cells. J Formos Med Assoc 2018; 117: 955–963 - PubMed
-
- Andrassy KM.Comments on ‘KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease’. Kidney Int 2013; 84: 622–623 - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer MA, Burdmann EA, Chen CY. et al. A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 2019–2032 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

