Preoperative prediction of pathological grade in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics
- PMID: 33630176
- PMCID: PMC7907291
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-021-00760-3
Preoperative prediction of pathological grade in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics
Abstract
Purpose: To develop and validate a machine learning model based on radiomic features derived from 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) images to preoperatively predict the pathological grade in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
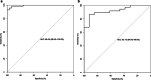
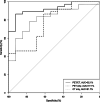
Methods: A total of 149 patients (83 men, 66 women, mean age 61 years old) with pathologically proven PDAC and a preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT scan between May 2009 and January 2016 were included in this retrospective study. The cohort of patients was divided into two separate groups for the training (99 patients) and validation (50 patients) in chronological order. Radiomics features were extracted from PET/CT images using Pyradiomics implemented in Python, and the XGBoost algorithm was used to build a prediction model. Conventional PET parameters, including standardized uptake value, metabolic tumor volume, and total lesion glycolysis, were also measured. The quality of the proposed model was appraised by means of receiver operating characteristics (ROC) and areas under the ROC curve (AUC).
Results: The prediction model based on a twelve-feature-combined radiomics signature could stratify PDAC patients into grade 1 and grade 2/3 groups with AUC of 0.994 in the training set and 0.921 in the validation set.
Conclusion: The model developed is capable of predicting pathological differentiation grade of PDAC based on preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics features.
Keywords: 18F-FDG PET/CT; Machine learning; Pancreatic cancer; Radiomics; XGBoost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

