Bounded Integer Modeling of Symptom Scales Specific to Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- PMID: 33630188
- PMCID: PMC7906927
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-021-00568-y
Bounded Integer Modeling of Symptom Scales Specific to Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Abstract
The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), the quality of life (QoL) score, and the benign prostatic hyperplasia impact index (BII) are three different scales commonly used to assess the severity of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH-LUTS). Based on a phase II clinical trial including 403 patients with moderate to severe BPH-LUTS, the objectives of this study were to (i) develop traditional pharmacometric and bounded integer (BI) models for the IPSS, QoL score, and BII endpoints, respectively; (ii) compare the power and type I error in detecting drug effects of BI modeling with traditional methods through simulation; and (iii) obtain quantitative translation between scores on the three abovementioned scales using a BI modeling framework. All developed models described the data adequately. Pharmacometric modeling using a continuous variable (CV) approach was overall found to be the most robust in terms of type I error and power to detect a drug effect. In most cases, BI modeling showed similar performance to the CV approach, yet severely inflated type I error was generally observed when inter-individual variability (IIV) was incorporated in the BI variance function (g()). BI modeling without IIV in g() showed greater type I error control compared to the ordered categorical approach. Lastly, a multiple-scale BI model was developed and estimated the relationship between scores on the three BPH-LUTS scales with overall low uncertainty. The current study yields greater understanding of the operating characteristics of the novel BI modeling approach and highlights areas potentially requiring further improvement.
Keywords: BPH; BPH impact index; International Prostate Symptom Score; LUTS; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.K.L and D.M.J. are employees of Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S. The authors report no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
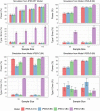
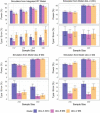
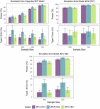
Similar articles
-
Tadalafil - a therapeutic option in the management of BPH-LUTS.Int J Clin Pract. 2014 Jan;68(1):94-103. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12305. Int J Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24341303 Review.
-
Construct validation of patient global impression of severity (PGI-S) and improvement (PGI-I) questionnaires in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia.BMC Urol. 2012 Nov 7;12:30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-12-30. BMC Urol. 2012. PMID: 23134716 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil Improves Symptoms, Erectile Function and Quality of Life in Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Suggestive of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (KYU-PRO Study).Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2018 Jan;10(1):76-83. doi: 10.1111/luts.12143. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2018. PMID: 29341501
-
Item Response Theory Modeling of the International Prostate Symptom Score in Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Associated with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.AAPS J. 2020 Aug 27;22(5):115. doi: 10.1208/s12248-020-00500-w. AAPS J. 2020. PMID: 32856168 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors for lower urinary tract symptoms consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia.BJU Int. 2019 Jul;124(1):27-34. doi: 10.1111/bju.14689. Epub 2019 Mar 11. BJU Int. 2019. PMID: 30681264
Cited by
-
Likelihood comparisons in bounded outcome score analysis must be internally consistent.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2024 Dec;51(6):577-579. doi: 10.1007/s10928-024-09933-8. Epub 2024 Jul 5. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2024. PMID: 38967731
-
Comparison of the power and type 1 error of total score models for drug effect detection in clinical trials.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2024 Dec 10;52(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s10928-024-09949-0. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2024. PMID: 39656313 Free PMC article.
-
A tutorial on pharmacometric Markov models.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;14(2):197-216. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13278. Epub 2024 Dec 13. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39670923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barry MJ, Fowler FJ, O’Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe HL, Mebust WK, Cockett ATK, The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol. 1992;148(5):1549–1557. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)36966-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for the non-clinical and clinical investigation of devices used for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) (2010). <https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents... Accessed March 20, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

