Beneficial Effects of a Perindopril/Indapamide Single-Pill Combination in Hypertensive Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity or Metabolic Syndrome: A Post Hoc Pooled Analysis of Four Observational Studies
- PMID: 33630277
- PMCID: PMC8004479
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-01619-8
Beneficial Effects of a Perindopril/Indapamide Single-Pill Combination in Hypertensive Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity or Metabolic Syndrome: A Post Hoc Pooled Analysis of Four Observational Studies
Abstract
Introduction: To assess real-life effectiveness of a perindopril/indapamide (Per/Ind) single-pill combination (SPC) in patients with hypertension (HT) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity and/or metabolic syndrome (MetS).
Methods: This post hoc analysis pooled raw data from four large observational studies (FORTISSIMO, FORSAGE, ACES, PICASSO). Patients, most with uncontrolled blood pressure (BP) on previous treatments were switched to Per/Ind (10 mg/2.5 mg) SPC at study entry. Office systolic and diastolic blood pressures (SBP and DBP) were measured at baseline, 1 month and 3 months.
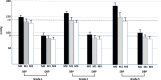
Results: In the overall pooled population (N = 16,763), mean age was 61 ± 12 years, HT duration 11 ± 8 years, and baseline SBP/DBP 162/94 mmHg. T2DM, obesity and MetS were present in 21%, 49% and 27% of patients, respectively. Subgroups had similar mean age and HT duration to the overall population; patients with T2DM were slightly older (64 ± 10 years) with a longer HT duration (13 ± 8 years). Mean BP was approximately 160/95 mmHg in each subgroup. At 1 month, mean SBP decreased by approximately 20 mmHg in the overall population, and by a further 10 mmHg at 3 months. Similar results were observed in the three subgroups, with mean changes from baseline at 3 months of - 28 ± 15/- 13 ± 10 in T2DM; - 30 ± 15/- 14 ± 10 in obesity; and - 31 ± 15/- 15 ± 9 mmHg in MetS. BP decreases were greatest in patients with grade II or grade III HT. BP control rates (< 140/90 mmHg or 140/85 mmHg for T2DM) at 3 months were 59% in T2DM, 67% in obese, and 66% in MetS. No specific safety concerns were raised, particularly concerning ionic (Na, K) or metabolic profiles.
Conclusions: Switching to Per/Ind SPC led to rapid and effective BP decreases in patients with T2DM, obesity, or MetS. BP control was achieved in 6-7 out of 10 previously treated but uncontrolled patients. Treatment was well tolerated. The results confirm the beneficial effects of a Per/Ind SPC for difficult-to-control patient populations.
Keywords: Blood pressure control; Hypertension; Indapamide; Metabolic syndrome; Obesity; Perindopril; Single-pill combination; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perindopril/Indapamide/Amlodipine in Hypertension: A Profile of Its Use.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2022 Mar;22(2):219-230. doi: 10.1007/s40256-022-00521-0. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35257306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Perindopril/Indapamide Single-Pill Combination in Uncontrolled Patients with Hypertension: A Pooled Analysis of the FORTISSIMO, FORSAGE, ACES and PICASSO Observational Studies.Adv Ther. 2021 Jan;38(1):479-494. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01527-3. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33150570
-
Full-dose Perindopril/Indapamide in the Treatment of Difficult-to-Control Hypertension: The FORTISSIMO Study.Clin Drug Investig. 2017 Feb;37(2):207-217. doi: 10.1007/s40261-016-0479-7. Clin Drug Investig. 2017. PMID: 27878562
-
Efficacy of single-pill perindopril/indapamide in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2014 Mar;21(1):63-9. doi: 10.1007/s40292-013-0036-x. Epub 2013 Dec 20. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2014. PMID: 24357222 Clinical Trial.
-
Very-low-dose combination of perindopril and indapamide: efficacy on blood pressure and target-organ damage.J Hypertens Suppl. 2003 Jun;21(3):S11-8. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200306003-00003. J Hypertens Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12929470 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-pill fixed-dose drug combinations to reduce blood pressure: the right pill for the right patient.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022 Jun 24;13:20406223221102754. doi: 10.1177/20406223221102754. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022. PMID: 35769133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy and Tolerability of a Fixed Combination of Perindopril and Indapamide in the Treatment of Unregulated Essential Hypertension - a Postmarketing Study.Acta Med Acad. 2022 Dec;51(3):163-174. doi: 10.5644/ama2006-124.385. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Acta Med Acad. 2022. PMID: 36799308 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Perindopril/Indapamide/Amlodipine in Hypertension: A Profile of Its Use.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2022 Mar;22(2):219-230. doi: 10.1007/s40256-022-00521-0. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35257306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44203. Accessed 2 Mar 2020.
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. Authors/Task Force Members. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36(10):1953–2041. - PubMed
-
- Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA. 2013;310(9):959–968. - PubMed
-
- Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75:1334–1357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical