Imipenem/Cilastatin/Relebactam: A Review in Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 33630278
- PMCID: PMC7905759
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-021-01471-8
Imipenem/Cilastatin/Relebactam: A Review in Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections
Abstract
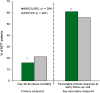
Imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam (Recarbrio™) is an intravenously administered combination of the carbapenem imipenem, the renal dehydropeptidase-I inhibitor cilastatin, and the novel β-lactamase inhibitor relebactam. Relebactam is a potent inhibitor of class A and class C β-lactamases, conferring imipenem activity against many imipenem-nonsusceptible strains. Imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam is approved in the USA and EU for the treatment of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia (HABP) and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (VABP) in adults and other gram-negative infections, including complicated urinary tract infections (cUTIs) [including pyelonephritis] and complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAIs), in adults with limited or no alternative treatment options. In pivotal phase II and III trials, imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam was noninferior to piperacillin/tazobactam in patients with HABP/VABP and to imipenem/cilastatin in patients with cUTIs and cIAIs. It was also effective in imipenem-nonsusceptible infections. Imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam was generally well tolerated, with a safety profile consistent with that of imipenem/cilastatin. Available evidence indicates that imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam is an effective and generally well tolerated option for gram-negative infections in adults, including critically ill and/or high-risk patients, and a potential therapy for infections caused by carbapenem-resistant pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
Young-A Heo is a salaried employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. Young-A Heo contributed to the review and is responsible for the article content.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics. 2017. https://www.who.int. Accessed 21 Dec 2020.
-
- Zhanel GG, Lawrence CK, Adam H, et al. Imipenem-relebactam and meropenem-vaborbactam: two novel carbapenem-beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations. Drugs. 2018;78(1):65–98. - PubMed
-
- Tabak YP, Sung AH, Ye G, et al. Attributable clinical and economic burden of carbapenem-non-susceptible gram-negative infections in patients hospitalized with complicated urinary tract infections. J Hosp Infect. 2019;102(1):37–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

