NT-proBNP Qualifies as a Surrogate for Clinical End Points in Heart Failure
- PMID: 33630302
- PMCID: PMC8360001
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.2222
NT-proBNP Qualifies as a Surrogate for Clinical End Points in Heart Failure
Abstract
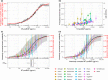
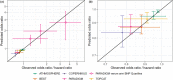
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is a well-established biomarker in heart failure (HF) but controversially discussed as a potential surrogate marker in HF trials. We analyzed the NT-proBNP/mortality relationship in real-world data (RWD) of 108,330 HF patients from the IBM Watson Health Explorys database and compared it with the NT-proBNP / clinical event end-point relationship in 20 clinical HF studies. With a hierarchical statistical model, we quantified the functional relationship and interstudy variability. To independently qualify the model, we predicted outcome hazard ratios in five phase III HF studies solely based on NT-proBNP measured early in the respective study. In RWD and clinical studies, the relationship between NT-proBNP and clinical outcome is well described by an Emax model. The NT-proBNP independent baseline risk (R0 , RWD/studies median (interstudy interquartile range): 5.5%/3.0% (1.7-4.9%)) is very low compared with the potential NT-proBNP-associated maximum risk (Rmax : 55.2%/79.4% (61.5-89.0%)). The NT-proBNP concentration associated with the half-maximal risk is comparable in RWD and across clinical studies (EC50 : 3,880/2,414 pg/mL (1,460-4,355 pg/mL)). Model-based predictions of phase III outcomes, relying on short-term NT-proBNP data only, match final trial results with comparable confidence intervals. Our analysis qualifies NT-proBNP as a surrogate for clinical outcome in HF trials. NT-proBNP levels after short treatment durations of less than 10 weeks quantitatively predict hazard ratios with confidence levels comparable to final trial readout. Early NT-proBNP measurement can therefore enable shorter and smaller but still reliable HF trials.
© 2021 Bayer AG. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employed by Bayer AG, a pharmaceutical company active in the development of heart failure treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NT-proBNP for Predicting All-Cause Death and Heart Transplant in Children and Adults with Heart Failure.Pediatr Cardiol. 2025 Mar;46(3):694-703. doi: 10.1007/s00246-024-03489-7. Epub 2024 May 9. Pediatr Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 38722325 Free PMC article.
-
NT-proBNP (N-Terminal pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide)-Guided Therapy in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: PRIMA II Randomized Controlled Trial (Can NT-ProBNP-Guided Therapy During Hospital Admission for Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Reduce Mortality and Readmissions?).Circulation. 2018 Apr 17;137(16):1671-1683. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029882. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29242350 Clinical Trial.
-
Interaction of Body Mass Index on the Association Between N-Terminal-Pro-b-Type Natriuretic Peptide and Morbidity and Mortality in Patients With Acute Heart Failure: Findings From ASCEND-HF (Acute Study of Clinical Effectiveness of Nesiritide in Decompensated Heart Failure).J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Feb 3;7(3):e006740. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006740. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29431103 Free PMC article.
-
N-Terminal B-type Natriuretic Peptide in Heart Failure.Heart Fail Clin. 2018 Jan;14(1):27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2017.08.004. Heart Fail Clin. 2018. PMID: 29153198 Review.
-
The predictive value of plasma biomarkers in discharged heart failure patients: role of plasma NT-proBNP.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016 Apr;64(2):157-64. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016. PMID: 26373781 Review.
Cited by
-
Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Vericiguat in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021 Nov;60(11):1407-1421. doi: 10.1007/s40262-021-01024-y. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021. PMID: 34086190 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating levels and prognostic cut-offs of sST2, hs-cTnT, and NT-proBNP in women vs. men with chronic heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Aug;9(4):2084-2095. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13883. Epub 2022 May 5. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35510529 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin Predicts Poor Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Low Levels of N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 17;14(12):1615. doi: 10.3390/biom14121615. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766322 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Blood Ultrafiltration Therapy in Patients with Acute Decompensated Chronic Heart Failure Running Title: Blood Ultrafiltration Therapy for Heart Failure.Physiol Res. 2023 Dec 31;72(6):701-706. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935073. Physiol Res. 2023. PMID: 38215058 Free PMC article.
-
Application Value of NT-proBNP Combined with NLR in Evaluation of Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Elderly Patients with Chronic Heart Failure.Emerg Med Int. 2022 Oct 14;2022:3689445. doi: 10.1155/2022/3689445. eCollection 2022. Emerg Med Int. 2022. Retraction in: Emerg Med Int. 2024 Jan 24;2024:9834523. doi: 10.1155/2024/9834523. PMID: 36275040 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Tang, W.H.W.B‐type natriuretic peptide: a critical review. Congest. Heart Fail. 13, 48–52 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski, P.et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 37, 2129–2200 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

