Down-regulation of RCC1 sensitizes immunotherapy by up-regulating PD-L1 via p27kip1 /CDK4 axis in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33630417
- PMCID: PMC8051708
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16383
Down-regulation of RCC1 sensitizes immunotherapy by up-regulating PD-L1 via p27kip1 /CDK4 axis in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
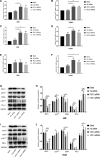
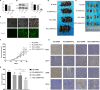
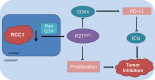
In recent years, although Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs) significantly improves survival both in local advanced stage and advanced stage of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the objective response rate of ICI monotherapy is still only about 20%. Thus, to identify the mechanisms of ICI resistance is critical to increase the efficacy of ICI treatments. By bioinformatics analysis, we found that the expression of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1) in lung adenocarcinoma was significantly higher than that in normal lung tissue in TCGA and Oncomine databases. The survival analysis showed that high expression RCC1 was associated with the poor prognosis of NSCLC. And the expression of RCC1 was inversely related to the number of immune cell infiltration. In vitro, knockdown of RCC1 not only significantly inhibited the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells but also increased the expression levels of p27kip1 and PD-L1, and decreased the expression level of CDK4 and p-Rb. In vivo, knockdown of RCC1 significantly slowed down the growth rate of tumour, and further reduced the volume and weight of tumour model after treated by PD-L1 monoclonal antibody. Therefore, RCC1 could up-regulate the expression level of PD-L1 by regulating p27kip1 /CDK4 pathway and decrease the resistance to ICIs. And this study might provide a new way to increase the efficacy of PD-L1 monoclonal antibody by inhibiting RCC1.
Keywords: ICI; PD-L1; RCC1; non-small cell lung cancer; p27KIP1/CDK4.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Switching administration of anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies as immune checkpoint inhibitor rechallenge in individuals with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Case series and literature review.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jul;11(7):1927-1933. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13483. Epub 2020 May 18. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32421224 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 expression and T cells infiltration in patients with uncommon EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer and the response to immunotherapy.Lung Cancer. 2020 Apr;142:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.02.010. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32120230
-
Elucidation of the relationships of MET protein expression and gene copy number status with PD-L1 expression and the immune microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2020 Mar;141:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31931443
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions.Oncologist. 2019 Feb;24(Suppl 1):S31-S41. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-IO-S1-s05. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30819829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nup50 plays more than one instrument.Cell Cycle. 2022 Sep;21(17):1785-1794. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2074742. Epub 2022 May 13. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35549614 Free PMC article.
-
RCC1 Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Colorectal Liver Oligometastases.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Dec 2;27:1610077. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.1610077. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34924821 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RCC1 to block the human soft-tissue sarcoma by disrupting nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of Skp2.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Apr 1;15(4):241. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06629-2. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38561375 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IDH3α Enhanced the Efficacy of Chemoimmunotherapy by Regulating Acidic Tumor Microenvironments.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;15(6):1802. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061802. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980689 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative and Comprehensive Pancancer Analysis of Regulator of Chromatin Condensation 1 (RCC1).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7374. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147374. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tumor Pathology Committee of Chinese Anti‐Cancer A , Expert Committee on Pathology of Chinese Society of Clinical O , Expert Committee on Non‐Small Cell Lung Cancer of Chinese Society of Clinical O . Expert consensus on PD‐L1 expression testing in non‐small‐cell lung cancer in China. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020;42(7):513‐521. 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200313-00202 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- cstc2018jcyjAX0012/the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, the Chongqing Science and Technology Commission
- cstc2015yfpt_gcj-syjzx120010/Chongqing Clinical Oncological Research Center, the Chongqing Science and Technology Commission
- 20141003/the Medical Scientific Research Project, Chongqing Health and Family Planning Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

