Peripapillary Hyper-reflective Ovoid Mass-like Structure (PHOMS): An Optical Coherence Tomography Marker of Axoplasmic Stasis in the Optic Nerve Head
- PMID: 33630781
- PMCID: PMC9258618
- DOI: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001203
Peripapillary Hyper-reflective Ovoid Mass-like Structure (PHOMS): An Optical Coherence Tomography Marker of Axoplasmic Stasis in the Optic Nerve Head
Abstract
Background: With the development and widespread adoption of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT), peripapillary hyper-reflective ovoid mass-like structures (PHOMS) have become a frequent OCT finding in neuro-ophthalmic practice. Although originally assumed to represent a form of buried optic disc drusen (ODD), PHOMS differ from ODD in many important ways. The histopathological underpinnings of PHOMS are now becoming more clearly understood.
Evidence acquisition: Review of literature.
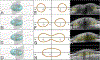
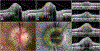
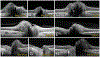
Results: PHOMS can be broadly classified as disk edema-associated PHOMS, ODD-associated PHOMS, or anomalous disk-associated PHOMS. PHOMS are seen in many conditions, including papilledema, nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, central retinal vein occlusion, acute demyelinating optic neuritis, ODD, and tilted disks (myopic obliquely inserted disks) and in many cases resolve along with the underlying condition. The histopathological study of these diverse entities reveals the common feature of a bulge of optic nerve fibers herniating centrifugally over Bruch membrane opening into the peripapillary space, correlating exactly with the location, shape, and space-occupying nature of PHOMS on OCT. Because of the radial symmetry of these herniating optic nerve fibers, PHOMS are best thought of as a complete or partial torus (i.e., donut) in 3 dimensions.
Conclusions: PHOMS are a common but nonspecific OCT marker of axoplasmic stasis in the optic nerve head. They are not themselves ODD or ODD precursors, although they can be seen in association with ODD and a wide spectrum of other conditions. They do not exclude papilledema and often accompany it. The circumferential extent and characteristic 3D toroidal nature of a PHOMS are best appreciated by scrolling through consecutive OCT images.
Copyright © 2021 by North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

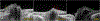
References
-
- Johnson LN, Diehl ML, Hamm CW, Sommerville DN, Petroski GF. Differentiating optic disc edema from optic nerve head drusen on optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 2009; 127:45–49. - PubMed
-
- Flores-Rodriguez P, Gili P, Martin-Rios MD. Sensitivity and specificity of time-domain and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in differentiating optic nerve head drusen and optic disc oedema. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2012; 32:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Wojtkowski M, Bajraszewski T, Gorczynska I, Targowski P, Kowalczyk A, Wasilewski W, Radzewicz C. Ophthalmic imaging by spectral optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2004; 138:412–419. - PubMed
-
- Nassif N, Cense B, Park BH, Yun SH, Chen TC, Bouma BE, Tearney GJ, de Boer JF. In vivo human retinal imaging by ultrahigh-speed spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett 2004; 29:480–482. - PubMed
-
- Spaide RF, Koizumi H, Pozonni MC. Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optic coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2008; 146:496–500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

