The anurans and squamates assemblage from Final Natufian Eynan (Ain Mallaha, Israel) with an emphasis on snake-human interactions
- PMID: 33630883
- PMCID: PMC7906325
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247283
The anurans and squamates assemblage from Final Natufian Eynan (Ain Mallaha, Israel) with an emphasis on snake-human interactions
Abstract
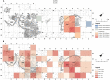
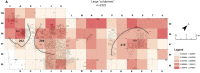
During the Natufian period, more than 12,000 years ago, Eynan (Ain Mallaha) was an important human settlement in the Hula Valley, Israel. This study concentrates on the anuran and squamate assemblage from the ultimate stage of the Natufian period at the site, the Final Natufian. Over five thousand bones assigned to at least sixteen taxa were studied from a sampled segment of the excavated open-air site. Relative species abundance, spatial distribution, taphonomic observations and ecological considerations all pointed to the conclusion that the inhabitants of Eynan intensively exploited three large "colubrine" snakes species: the Large Whip Snake (Dolichophis jugularis), the Eastern Montpellier Snake (Malpolon insignitus) and an Eastern Four-lined Ratsnake (Elaphe cf. sauromates). These snakes were the most desired and were intensively gathered, while other snakes and lizards could have been opportunistically collected when encountered. We raise questions about whether the large "colubrines" exploitation should be interpreted as additional evidence of increasing diet breadth. We suggest challenging this line of reasoning and offer possible alternative motives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


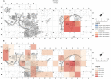



Similar articles
-
Squamate bone taphonomy: A new experimental framework and its application to the Natufian zooarchaeological record.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 10;10(1):9373. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66301-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32523029 Free PMC article.
-
A New Look at Shelter 131/51 in the Natufian Site of Eynan (Ain-Mallaha), Israel.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 8;10(7):e0130121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130121. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26154433 Free PMC article.
-
Bone aerophones from Eynan-Mallaha (Israel) indicate imitation of raptor calls by the last hunter-gatherers in the Levant.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 9;13(1):8709. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35700-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37296190 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of the South American fossil squamates.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 Mar;297(3):349-68. doi: 10.1002/ar.22858. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 24482358 Review.
-
Structure and function of the hearts of lizards and snakes.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2014 May;89(2):302-36. doi: 10.1111/brv.12056. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2014. PMID: 23998743 Review.
Cited by
-
A new, rare, small-ranged, and endangered mountain snake of the genus Elaphe from the Southern Levant.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 24;13(1):4839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30878-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36964263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burghardt GM, Murphy JB, Chiszar D, Hutchins M. Combating ophiophobia: Origins, treatment, education, and conservation tools. In: Mulin SJ, Seigal A, editors. Snakes ecology and conservation. New York: Cornell University Press; 2009. pp. 262–280.
-
- Werner YL. Reptile life in the land of Israel. Frankfurt am Main: Edition Chimaira; 2016.
-
- Enzel Y, Bar-Yosef O. Quaternary of the Levant: environments, climate change, and humans: Part III: archaeology of human evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2017. pp. 179–328.
-
- Stiner MC. The faunas of Hayonim Cave, Israel: A 200,000-year record of paleolithic diet, demography, and society. Cambridge: American School of Prehistoric Research Bulletin, Peabody Museum; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

