Indirect immunofluorescence for detecting anti-neuronal autoimmunity in CSF after COVID-19 - Possibilities and pitfalls
- PMID: 33631284
- PMCID: PMC9761871
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.02.013
Indirect immunofluorescence for detecting anti-neuronal autoimmunity in CSF after COVID-19 - Possibilities and pitfalls
Figures
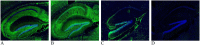
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor: Comment on Mulder J et al. (2021) indirect immunofluorescence for detecting anti-neuronal autoimmunity in CSF after COVID-19 - possibilities and pitfalls.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 May;94:475. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.02.014. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33639240 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
High frequency of cerebrospinal fluid autoantibodies in COVID-19 patients with neurological symptoms.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Mar;93:415-419. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.022. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33359380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franke C., Ferse C., Kreye J., Reincke S.M., Sanchez-Sendin E., Rocco A., Steinbrenner M., Angermair S., Treskatsch S., Zickler D., Eckardt K.-U., Dersch R., Hosp J., Audebert H.J., Endres M., Ploner J.C., Prüß H. High frequency of cerebrospinal fluid autoantibodies in COVID-19 patients with neurological symptoms. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Virhammar J., Kumlien E., Fällmar D., Frithiof R., Jackmann S., Sköld M.K., Kadir M., Frick J., Lindeberg J., Olivero-Reinius H., Ryttlefors M., Cunningham J.L., Wikström J., Grabowska A., Bondeson K., Bergquist J., Zetterberg H., Rostami E. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy with SARS-CoV-2 RNA confirmed in cerebrospinal fluid. Neurology. 2020;95(10):445–449. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010250. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mulder J., Feresiadou A., Fallmar D., Frithiof R., Virhammar J., Rasmusson J.A., Rostami E., Kumlien E., Cunningham L.J. Autoimmune encephalitis presenting with acute excited catatonia in a 40-year-old male patient with Covid-19. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2020 doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20081236. In press. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sjostedt, E., Zhong, W., Fagerberg, L., et al. An atlas of the protein-coding genes in the human, pig, and mouse brain. Science. 2020;367(6482). doi: 10.1126/science.aay5947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

