Arabidopsis natural variation in insect egg-induced cell death reveals a role for LECTIN RECEPTOR KINASE-I.1
- PMID: 33631806
- PMCID: PMC8133593
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiaa022
Arabidopsis natural variation in insect egg-induced cell death reveals a role for LECTIN RECEPTOR KINASE-I.1
Abstract
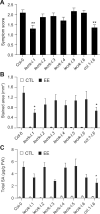
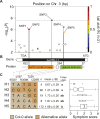
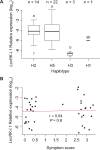
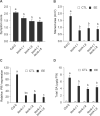
In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), a hypersensitive-like response (HR-like response) is triggered underneath the eggs of the large white butterfly Pieris brassicae (P. brassicae), and this response is dependent on salicylic acid (SA) accumulation and signaling. Previous reports indicate that the clade I L-type LECTIN RECEPTOR KINASE-I.8 (LecRK-I.8) is involved in early steps of egg recognition. A genome-wide association study was used to better characterize the genetic structure of the HR-like response and discover loci that contribute to this response. We report here the identification of LecRK-I.1, a close homolog of LecRK-I.8, and show that two main haplotypes that explain part of the variation in HR-like response segregate among natural Arabidopsis accessions. Besides, signatures of balancing selection at this locus suggest that it may be ecologically important. Disruption of LecRK-I.1 results in decreased HR-like response and SA signaling, indicating that this protein is important for the observed responses. Furthermore, we provide evidence that LecRK-I.1 functions in the same signaling pathway as LecRK-I.8. Altogether, our results show that the response to eggs of P. brassicae is controlled by multiple LecRKs.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2020. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Ariga H, Katori T, Tsuchimatsu T, Hirase T, Tajima Y, Parker JE, Alcázar R, Koornneef M, Hoekenga O, Lipka AE, et al. (2017) NLR locus-mediated trade-off between abiotic and biotic stress adaptation in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 3: 17072. - PubMed
-
- Bittner N, Trauer-Kizilelma U, Hilker M (2017) Early plant defence against insect attack: involvement of reactive oxygen species in plant responses to insect egg deposition. Planta 245: 993–1007 - PubMed
-
- Blenn B, Bandoly M, Küffner A, Otte T, Geiselhardt S, Fatouros NE, Hilker M (2012) Insect egg deposition induces indirect defense and epicuticular wax changes in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Chem Ecol 38: 882–892 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

