Belimumab for systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 33631841
- PMCID: PMC8095005
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010668.pub2
Belimumab for systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Belimumab, the first biologic approved for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), has been shown to reduce autoantibody levels in people with SLE and help control disease activity.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of belimumab (alone or in combination) in systematic lupus erythematosus.
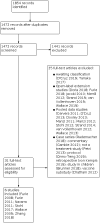
Search methods: An Information Specialist carried out the searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Web of Science, the World Health Organization (WHO) International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and clinicaltrials.gov from inception to 25 September 2019. There were no language or date restrictions.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or controlled clinical trials (CCTs) of belimumab (alone or in combination) compared to placebo/control treatment (immunosuppressive drugs, such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil or another biologic), in adults with SLE.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodologic procedures expected by Cochrane.
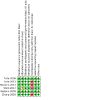
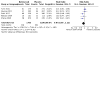
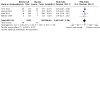
Main results: Six RCTs (2917 participants) qualified for quantitative analyses. All included studies were multicenter, international or US-based. The age range of the included participants was 22 to 80 years; most were women; and study duration ranged from 84 days to 76 weeks. The risk of bias was generally low except for attrition bias, which was high in 67% of studies. Compared to placebo, more participants on belimumab 10 mg/kg (Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved dose) showed at least a 4-point improvement (reduction) in Safety of Estrogen in Lupus National Assessment (SELENA) - Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) score, a validated SLE disease activity index: (risk ratio (RR) 1.33, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.22 to 1.45; 829/1589 in belimumab group and 424/1077 in placebo; I2= 0%; 4 RCTs; high-certainty evidence). Change in health-related quality of life (HRQOL), assessed by Short Form-36 Physical Component Summary score improvement (range 0 to 100), showed there was probably little or no difference between groups (mean difference 1.6 points, 95% CI 0.30 to 2.90; 401 in belimumab group and 400 in placebo; I2= 0%; 2 RCTs; moderate-certainty evidence). The belimumab 10 mg/kg group showed greater improvement in glucocorticoid dose, with a higher proportion of participants reducing their dose by at least 50% compared to placebo (RR 1.59, 95% CI 1.17 to 2.15; 81/269 in belimumab group and 52/268 in placebo; I2= 0%; 2 RCTs; high-certainty evidence). The proportion of participants experiencing harm may not differ meaningfully between the belimumab 10 mg/kg and placebo groups: one or more serious adverse event (RR 0.87, 95% CI: 0.68 to 1.11; 238/1700 in belimumab group and 199/1190 in placebo; I2= 48%; 5 RCTs; low-certainty evidence; ); one or more serious infection (RR 1.01, 95% CI: 0.66 to 1.54; 44/1230 in belimumab group and 40/955 in placebo; I2= 0%; 4 RCTs; moderate-certainty evidence); and withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 0.82, 95% CI: 0.63 to 1.07; 113/1700 in belimumab group and 94/1190 in placebo; I2= 0%; 5 RCTs; moderate-certainty evidence). Mortality was rare, and may not differ between belimumab 10 mg/kg and placebo (Peto odds ratio 1.15, 95% CI 0.41 to 3.25; 9/1714 in belimumab group and 6/1203 in placebo; I2= 4%; 6 RCTs; low-certainty evidence).
Authors' conclusions: The six studies that provided evidence for benefits and harms of belimumab were well-designed, high-quality RCTs. At the FDA-approved dose of 10 mg/kg, based on moderate to high-certainty data, belimumab was probably associated with a clinically meaningful efficacy benefit compared to placebo in participants with SLE at 52 weeks. Evidence related to harms is inconclusive and mostly of moderate to low-certainty evidence. More data are needed for the longer-term efficacy of belimumab.
Copyright © 2021 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JAS: JAS has received consultant fees from Crealta/Horizon, Medisys, Fidia, UBM LLC, Trio Health, Medscape, WebMD, Adept Field Solutions, Clinical Care options, Clearview healthcare partners, Putnam associates, Focus forward, Navigant consulting, Spherix, Practice Point communications, the National Institutes of Health and the American College of Rheumatology. JAS owns stock options in TPT Global Tech, Vaxart pharmaceuticals and Charlotte’s Web Holdings, Inc. JAS previously owned stock options in Amarin, Viking and Moderna pharmaceuticals. JAS is on the speaker’s bureau of Simply Speaking. JAS is a member of the executive of Outcomes Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT), an organization that develops outcome measures in rheumatology and receives arms‐length funding from 12 companies. JAS serves on the FDA Arthritis Advisory Committee. JAS is the chair of the Veterans Affairs Rheumatology Field Advisory Committee. JAS is the editor and the Director of the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group Satellite Center on Network Meta‐analysis. JAS previously served as a member of the following committees: member, the American College of Rheumatology's (ACR) Annual Meeting Planning Committee (AMPC) and Quality of Care Committees, the Chair of the ACR Meet‐the‐Professor, Workshop and Study Group Subcommittee and the co‐chair of the ACR Criteria and Response Criteria subcommittee.
NS: none
AM: none
Figures






Comment in
-
What are the benefits and harms of belimumab for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus?: A Cochrane Review summary with commentary.Int J Rheum Dis. 2021 Oct;24(10):1331-1333. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14214. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 34523249 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Furie 2008 {published data only}
-
- Furie R, Stohl W, Ginzler EM, Becker M, Mishra N, Chatham W, et al. Biologic activity and safety of belimumab, a neutralizing anti-B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) monoclonal antibody: a phase I trial in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Research and Therapy 2008;5:R109. - PMC - PubMed
Furie 2011 {published data only}
-
- Furie R, Petri M, Zamani O, Cervera R, Wallace DJ, Tegzova D, et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2011;63(12):3918-30. - PMC - PubMed
Navarra 2011 {published data only}
-
- Navarra SV, Guzman RM, Gallacher AE, Hall S, Levy RA, Jimenez RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011;377(9767):721-31. - PubMed
Stohl 2017 {published data only}
Wallace 2009 {published data only}
Zhang 2018 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Brunner 2018 {published data only}
-
- Brunner HI, Abud-Mendoza C, Viola DO, Calvo Penades I, Levy D, Anton J, et al. Efficacy and safety of intravenous belimumab in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatology 2018;70(Supplement 9):3225-6.
Cervera 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cervera R, Strand V, Levy RA, Petri M, Rudge H, Hough D, et al. Belimumab improved fatigue and SF-36 physical/mental component summary scores in SLE: BLISS-52/BLISS-76. Lupus 2011;20(4):425.
Chatham 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chatham WW, Wallace DJ, Stohl W, Latinis KM, Manzi S, McCune WJ, et al. Effect of belimumab on vaccine antigen antibodies to influenza, pneumococcal, and tetanus vaccines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in the BLISS-76 trial. Journal of Rheumatology 2012;39(8):1632-40. - PubMed
D'Cruz 2013 {published data only}
-
- D'Cruz D, Gladman D, Navarra SV, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Manzi S, Freimuth WW. Post Hoc British Isles Lupus Assessment Group Index musculoskeletal organ domain analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus patients in phase 3 belimumab trials. Lupus 2013;22(1):106.
Dooley 2013 {published data only}
-
- Dooley MA, Houssiau F, Aranow C, D'Cruz DP, Askanase A, Roth DA, et al. Effect of belimumab treatment on renal outcomes: results from the phase 3 belimumab clinical trials in patients with SLE. Lupus 2013;22(1):63-72. - PubMed
Doria 2018 {published data only}
Furie 2018 {published data only}
-
- Furie RA, Wallace DJ, Aranow C, Fettiplace J, Wilson B, Mistry P, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a continuation of a seventy-six-week phase III parent study in the United States. Arthritis and Rheumatology 2018;70(6):868-77. - PMC - PubMed
Gamble 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gamble RG, Dellavalle RP. A randomized controlled trial of belimumab for the treatment of active systemic lupus erythematosus. Archives of Dermatology 2012;148(3):376-8. - PubMed
Jacobi 2010 {published data only}
Manzi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Manzi S, Gladman D, Navarra S, Sanchez-Guerrero J, D'Cruz D, Freimuth W, et al. Post Hoc British Isles Lupus Assessment Group Index mucocutaneous organ domain item analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus patients treated in phase 3 belimumab clinical trials.. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2011;63 (10 Suppl):S231.
Manzi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Manzi S, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Merrill JT, Furie R, Gladman D, Navarra SV, et al. Effects of belimumab, a B lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, on disease activity across multiple organ domains in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: combined results from two phase III trials. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2012;71(11):1833-8. - PMC - PubMed
Merrill 2012 {published data only}
-
- Merrill JT, Ginzler EM, Wallace DJ, McKay JD, Lisse JR, Aranow C, et al. Long-term safety profile of belimumab plus standard therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2012;64(10):3364-73. - PubMed
Onno‐Teng 2019 {published data only}
-
- Teng YK, Bruce IN, Diamond B, Furie RA, Vollenhoven RF, Gordon D, et al. Phase III, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 104-week study of subcutaneous belimumab administered in combination with rituximab in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): BLISS-BELIEVE study protocol. BMJ Open 2019;9(3):e025687. - PMC - PubMed
Petri 2013 {published data only}
-
- Petri MA, Van Vollenhoven RF, Buyon J, Levy RA, Navarra SV, Cervera R, et al. Baseline predictors of systemic lupus erythematosus flares: data from the combined placebo groups in the phase III belimumab trials. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2013;65(8):2143-53. - PubMed
Rademacher 2018 {published data only}
-
- Rademacher JG, Schrempf LE, Pluss M, Muller GA, Korsten P. Therapeutic efficacy of belimumab in addition to standard therapy for lupus nephritis and neuropsychiatric lupus-case series of routinely collected data at a single centre. Lupus Science and Medicine 2018;5(Supplement 1):A119-20.
Stohl 2012 {published data only}
Strand 2014 {published data only}
-
- Strand V, Levy RA, Cervera R, Petri MA, Birch H, Freimuth WW, et al. Improvements in health-related quality of life with belimumab, a B-lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, in patients with autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus from the randomised controlled BLISS trials. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases May 2014;73(5):838-44. - PMC - PubMed
Strand 2019 {published data only}
van Vollenhoven 2012 {published data only}
van Vollenhoven 2019 {published data only}
von Kempis 2019 {published data only}
-
- Kempis J, Duetsch S, Reuschling N, Villiger R, Villiger PM, Vallelian F, et al. Clinical outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with belimumab in clinical practice settings: a retrospective analysis of results from the OBSErve study in Switzerland. Swiss Medical Weekly 2019;149:w20022. - PubMed
Wallace 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wallace DJ, Navarra S, Petri MA, Gallacher A, Thomas M, Furie R, et al. Safety profile of belimumab: pooled data from placebo-controlled phase 2 and 3 studies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2013;22(2):144-54. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
D'Cruz 2019 {published data only}
-
- D'Cruz D, Maksimowicz-McKinnon K, Oates J, Santiago MB, Bass D, Burriss S, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients of black race with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from the embrace study. Lupus Science and Medicine 2019;6(Supplement 1):A149-50.
Tanaka 2017 {published data only}
-
- Tanaka Y, Bass D, Chu M, Egginton S, Ji B, Pobiner B, et al. Effects of belimumab on corticosteroid use in a pivotal phase III, randomised, placebo controlled study in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus in North East Asia. Lupus Science and Medicine 2017;4(Supplement 1):A45-6.
Additional references
Blair 2018
-
- Blair HA, Duggan ST. Belimumab: a review in systemic lupus erythematosus. Drugs 2018;78(3):355-66. - PubMed
Bossen 2006
-
- Bossen C, Schneider P. BAFF, APRIL and their receptors: structure, function and signaling. Seminars in Immunology 2006;18(5):263-75. - PubMed
Boyce 2012
-
- Boyce EG, Fusco BE. Belimumab: review of use in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Therapeutics 2012;34(5):1006-22. - PubMed
Burness 2011
-
- Burness CB, McCormack PL. Belimimab: in systemic lupus erythematosus. Drugs 2011;71(18):2435-44. - PubMed
Cates 2004
-
- Cates C. EBM Web Site. Visual Rx Version 3 (accessed October 2011) [Computer program]. Available from: www.nntonline.net/visualrx 2004.
Cheema 2001
-
- Cheema GS, Roschke V, Hilbert DM, Stohl W. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2001;44:1313–9. - PubMed
Collins 2006
-
- Collins CE, Gavin AL, Migone T-S, Hilbert DM, Nemazee D, Stohl W. B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) isoforms in systemic lupus erythematosus: disease activity correlates better with blood leukocyte BLyS mRNA levels than with plasma BLyS protein levels. Arthritis Research and Therapy 2006;8:R6. - PMC - PubMed
Crow 2004
-
- Crow M, Kirou KA. Interferon-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2004;16:541-7. - PubMed
Crowley 2005
-
- Crowley JE, Treml LS, Stadanlick JE, Carpenter E, Cancro MP. Homeostatic niche specification among naive and activated B cells: a growing role for the BLyS family of receptors and ligands. Seminars in Immunology 2005;17(3):193-9. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), Accessed October 2019. Available at gradepro.org.
Hay 1993
-
- Hay EM, Bacon PA, Gordon C, Isenberg DA, Maddison P, Snaith ML, et al. The BILAG index: a reliable and valid instrument for measuring clinical disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1993;86(7):447-58. - PubMed
Higgins 2020
-
- Higgins JPT, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane, 2020.. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook..
Hochberg 1997
-
- Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1997;40(9):1725. - PubMed
Isenberg 2000
-
- Isenberg DA, Gordon C. From BILAG to BLIPS - disease activity assessment in lupus past, present and future. Lupus 2000;9(9):651-4. - PubMed
Kandala 2013
Kim 2009
Kim 2012
Lee 2018
-
- Lee YH, Song GG. Comparative efficacy and safety of intravenous or subcutaneous belimumab in combination with standard therapy in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lupus 2018;27(1):112-119. - PubMed
Litinskiy 2002
Petri 1999
-
- Petri M, Buyon J, Kim M. Classification and definition of major flares in SLE clinical trials. Lupus 1999;8(8):685-91. - PubMed
Petri 2005
-
- Petri M, Kim MY, Kalunian KC, Grossman J, Hahn BH, Sammaritano LR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(24):2550-8. - PubMed
Petri 2008
-
- Petri M, Stohl W, Chatham W, McCune WJ, Chevrier M, Ryel J, et al. Association of plasma B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) levels and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;58:2453–9. - PubMed
Ravirajan 1996
Schunemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Schunemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

