Identification and elimination of genomic regions irrelevant for magnetosome biosynthesis by large-scale deletion in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense
- PMID: 33632118
- PMCID: PMC7908775
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-021-02124-2
Identification and elimination of genomic regions irrelevant for magnetosome biosynthesis by large-scale deletion in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense
Abstract
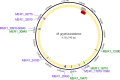
Background: Magnetosome formation in the alphaproteobacterium Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense is controlled by more than 30 known mam and mms genes clustered within a large genomic region, the 'magnetosome island' (MAI), which also harbors numerous mobile genetic elements, repeats, and genetic junk. Because of the inherent genetic instability of the MAI caused by neighboring gene content, the elimination of these regions and their substitution by a compact, minimal magnetosome expression cassette would be important for future analysis and engineering. In addition, the role of the MAI boundaries and adjacent regions are still unclear, and recent studies indicated that further auxiliary determinants for magnetosome biosynthesis are encoded outside the MAI. However, techniques for large-scale genome editing of magnetic bacteria are still limited, and the full complement of genes controlling magnetosome formation has remained uncertain.
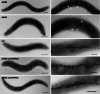
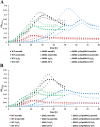
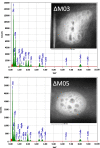
Results: Here we demonstrate that an allelic replacement method based on homologous recombination can be applied for large-scale genome editing in M. gryphiswaldense. By analysis of 24 deletion mutants covering about 167 kb of non-redundant genome content, we identified genes and regions inside and outside the MAI irrelevant for magnetosome biosynthesis. A contiguous stretch of ~ 100 kb, including the scattered mam and mms6 operons, could be functionally substituted by a compact and contiguous ~ 38 kb cassette comprising all essential biosynthetic gene clusters, but devoid of interspersing irrelevant or problematic gene content.
Conclusions: Our results further delineate the genetic complement for magnetosome biosynthesis and will be useful for future large-scale genome editing and genetic engineering of magnetosome biosynthesis.
Keywords: Genome reduction; Magnetosomes; Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Towards a 'chassis' for bacterial magnetosome biosynthesis: genome streamlining of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense by multiple deletions.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Feb 4;20(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01517-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33541381 Free PMC article.
-
Overproduction of Magnetosomes by Genomic Amplification of Biosynthesis-Related Gene Clusters in a Magnetotactic Bacterium.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 May 2;82(10):3032-3041. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03860-15. Print 2016 May 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26969709 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of the mamAB and mms6 operons reveals a gene set essential for magnetosome biogenesis in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jul;196(14):2658-69. doi: 10.1128/JB.01716-14. Epub 2014 May 9. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24816605 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of a subcellular compartment: the magnetosome membrane in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense.Arch Microbiol. 2004 Jan;181(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00203-003-0631-7. Epub 2003 Dec 11. Arch Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14668979 Review.
-
Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Sep 13;14(10):621-37. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.99. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27620945 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a 'chassis' for bacterial magnetosome biosynthesis: genome streamlining of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense by multiple deletions.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Feb 4;20(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01517-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33541381 Free PMC article.
-
Functional expression of foreign magnetosome genes in the alphaproteobacterium Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0328222. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03282-22. Epub 2023 Jun 15. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37318230 Free PMC article.
-
MamF-like proteins are distant Tic20 homologs involved in organelle assembly in bacteria.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 9;15(1):10657. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55121-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39653729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schleifer KH, Schüler D, Spring S, Weizenegger M, Amann R, Ludwig W, Köhler M. The genus Magnetospirillum gen. Nov. description of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense sp. nov. and transfer of Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum to Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum comb. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1991;14:379–385. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80313-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

