Anthropometric measures of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease risk in the Eastern Caribbean Health Outcomes Research Network (ECHORN) Cohort Study
- PMID: 33632164
- PMCID: PMC7905572
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-10399-3
Anthropometric measures of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease risk in the Eastern Caribbean Health Outcomes Research Network (ECHORN) Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Accurately defining obesity using anthropometric measures that best capture obesity-related risk is important for identifying high risk groups for intervention. The purpose of this study is to compare the association of different anthropometric measures of obesity with 10-year cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in adults in the Eastern Caribbean.
Methods: Data from the Eastern Caribbean Health Outcomes Research Network (ECHORN) Cohort Study (ECS) were analyzed. The ECS is comprised of adults aged 40 and older residing in the US Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico, Barbados, and Trinidad. 10-year CVD risk was calculated using the American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) ASCVD Risk Algorithm and categorized in the following high-risk groups: > 7.5, > 10, and > 20%. Logistic regression was used to examine associations between four anthropometric measures of obesity (BMI, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, waist-to height ratio) and 10-year CVD risk.
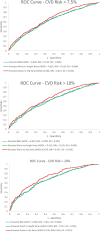
Results: Mean age (SD) of participants (n = 1617) was 56.6 years (±10.2), 64% were women, 74% were overweight/obese, and 24% had an ASCVD risk score above 10%. Elevated body mass index (BMI, > 30 kg/m2) and waist circumference were not associated with CVD risk. Elevated waist-to-hip ratio (WHR, > 0.9 men, > 0.85 women) and elevated waist-to-height ratio (> 0.5) were associated with all three categories of CVD risk. Area under the receiver curve was highest for WHR for each category of CVD risk. Elevated WHR demonstrated odds of 2.39, 2.58, and 3.32 (p < 0.0001) for CVD risk of > 7.5, > 10 and > 20% respectively.
Conclusion: Findings suggest that WHR is a better indicator than BMI of obesity-related CVD risk and should be used to target adults in the Caribbean, and of Caribbean-descent, for interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determining the best method for evaluating obesity and the risk for non-communicable diseases in women of childbearing age by measuring the body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, waist-to-height ratio, A Body Shape Index, and hip index.Nutrition. 2023 Oct;114:112135. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2023.112135. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Nutrition. 2023. PMID: 37453224
-
Ethnicity and the association between anthropometric indices of obesity and cardiovascular risk in women: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2014 May 22;4(5):e004702. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004702. BMJ Open. 2014. PMID: 24852299 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and cardiovascular disease risk among Africans residing in Europe and Africa: the RODAM study.Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Mar-Apr;14(2):151-157. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32061582
-
Associations of obesity indices change with cardiovascular outcomes: a dose-response meta-analysis.Int J Obes (Lond). 2024 May;48(5):635-645. doi: 10.1038/s41366-024-01485-8. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38336864 Review.
-
Scoping review report: obesity in older adults.Int J Obes (Lond). 2012 Sep;36(9):1141-50. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2012.29. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22410960
Cited by
-
Classification of blood pressure during sleep impacts designation of nocturnal nondipping.PLOS Digit Health. 2023 Jun 13;2(6):e0000267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000267. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLOS Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37310958 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Anti-Neoplastic Effects of Curcumin and Urogenital Cancers: A Systematic Review.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Oct 15;2024:9347381. doi: 10.1155/2024/9347381. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39445208 Free PMC article.
-
Neighbourhood Walkability and Its Influence on Physical Activity and Cardiometabolic Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Caribbean Small Island Developing State.Cureus. 2023 Aug 24;15(8):e44060. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44060. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37746352 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes prevention in the Caribbean using Lifestyle Intervention and Metformin Escalation (LIME): Protocol for a hybrid Type-1 effectiveness-implementation trial using a quasi-experimental study design.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2021 Mar 11;22:100750. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2021.100750. eCollection 2021 Jun. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2021. PMID: 33997458 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Waist-Hip Ratio and Female Infertility in the United States: Data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017-2020.Obes Facts. 2024;17(5):445-458. doi: 10.1159/000538974. Epub 2024 May 2. Obes Facts. 2024. PMID: 38697046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vos T, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong Y, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2006;113(6):898–918. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.171016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

