UTRN inhibits melanoma growth by suppressing p38 and JNK/c-Jun signaling pathways
- PMID: 33632212
- PMCID: PMC7905598
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01768-4
UTRN inhibits melanoma growth by suppressing p38 and JNK/c-Jun signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: Utrophin (UTRN), as a tumor suppressor gene, is involved in various cancer progression. The function of UTRN in the melanoma process and the related molecular mechanisms are still unclear. Herein, we studied the function of UTRN in melanoma growth and the relevant molecular mechanisms.
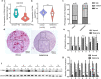
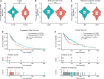
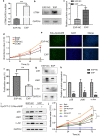
Methods: Using the GEO database and UCSC Xena project, we compared the expression of UTRN in non-cancerous and melanoma tissues. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining, qRT-PCR and Western Blot (WB) were performed to evaluate UTRN expression in clinical samples. A total of 447 cases with UTRN expression data, patient characteristics and survival data were extracted from TCGA database and analyzed. After stable transduction and single cell cloning, the proliferation ability of A375 human melanoma cells was analyzed by Cell Counting Kit‑8 (CCK) and 5‑ethynyl‑2'‑deoxyuridine (EdU) incorporation assays. GSEA was performed to predict the mechanism by which UTRN regulated melanoma growth. Then WB analysis was used to assess the protein expression levels of pathway signaling in overexpression (EXP) melanoma cells. Epac activator 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP was then used to evaluate the proliferation ability by activation of p38 and JNK/c-Jun signaling pathways.
Results: Data from GEO and UCSC Xena project indicated that UTRN expression was decreased in melanoma. Experiment on clinical samples further confirmed our finding. TCGA results showed that a reduced expression of UTRN in 447 melanoma samples was associated with advanced clinical characteristics (T stage, Clark level, ulceration), shorter survival time and poorer prognosis. In addition, up-regulated UTRN expression inhibited melanoma cell proliferation when compared to control group. MAPK signaling pathway was presented in both KEGG and BioCarta databases by using GSEA tool. WB results confirmed the down-regulated expression of p38, JNK1 and c-Jun in EXP group when compared to control group. Epac activator 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP treatment could partially rescue proliferation of tumor cells.
Conclusion: We have demonstrated that reduced UTRN predicted poorer prognosis and UTRN inhibited melanoma growth via p38 and JNK1/c-Jun pathways. Therefore, UTRN could serve as a tumor suppressor and novel prognostic biomarker for melanoma patients.
Keywords: GSEA; Melanoma; Survival analysis; TCGA; UTRN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SHARPIN Promotes Melanoma Progression via Rap1 Signaling Pathway.J Invest Dermatol. 2020 Feb;140(2):395-403.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.07.696. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Invest Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31401046
-
Differential Gene Expression and Methylation Analysis of Melanoma in TCGA Database to Further Study the Expression Pattern of KYNU in Melanoma.J Pers Med. 2022 Jul 25;12(8):1209. doi: 10.3390/jpm12081209. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35893303 Free PMC article.
-
UTRN on chromosome 6q24 is mutated in multiple tumors.Oncogene. 2007 Sep 13;26(42):6220-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210432. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17384672
-
Long non-coding RNA miR143HG predicts good prognosis and inhibits tumor multiplication and metastasis by suppressing mitogen-activated protein kinase and Wnt signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatol Res. 2019 Aug;49(8):902-918. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13344. Epub 2019 May 30. Hepatol Res. 2019. PMID: 30945380
-
Tetraspanin CD9 induces MMP-2 expression by activating p38 MAPK, JNK and c-Jun pathways in human melanoma cells.Exp Mol Med. 2005 Jun 30;37(3):230-9. doi: 10.1038/emm.2005.31. Exp Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16000878
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Genomic Analysis of Puerarin in Inhibiting Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Migration.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024;19(4):516-529. doi: 10.2174/1574892819666230908110107. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 37694778 Free PMC article.
-
UTRN as a potential biomarker in breast cancer: a comprehensive bioinformatics and in vitro study.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 2;14(1):7702. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58124-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38565593 Free PMC article.
-
The Essential Oil from Conyza bonariensis (L.) Cronquist (Asteraceae) Exerts an In Vitro Antimelanoma Effect by Inducing Apoptosis and Modulating the MAPKs, NF-κB, and PKB/AKT Signaling Pathways.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1553. doi: 10.3390/ph16111553. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004419 Free PMC article.
-
PSPH promotes the proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through MAPK signaling pathways.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 25;15(4):1919-1931. doi: 10.62347/OGMW9514. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40371136 Free PMC article.
-
Computed cancer interactome explains the effects of somatic mutations in cancers.Protein Sci. 2022 Dec;31(12):e4479. doi: 10.1002/pro.4479. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 36261849 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

