Trans-synaptic spreading of alpha-synuclein pathology through sensory afferents leads to sensory nerve degeneration and neuropathic pain
- PMID: 33632316
- PMCID: PMC7905893
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-021-01131-8
Trans-synaptic spreading of alpha-synuclein pathology through sensory afferents leads to sensory nerve degeneration and neuropathic pain
Abstract
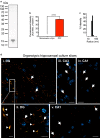
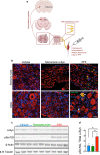
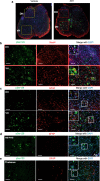
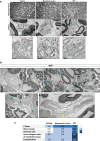
Pain is a common non-motor symptom of Parkinson's disease (PD), with current limited knowledge of its pathophysiology. Here, we show that peripheral inoculation of mouse alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) pre-formed fibrils, in a transgenic mouse model of PD, elicited retrograde trans-synaptic spreading of α-Syn pathology (pSer129) across sensory neurons and dorsal nerve roots, reaching central pain processing regions, including the spinal dorsal horn and the projections of the anterolateral system in the central nervous system (CNS). Pathological peripheral to CNS propagation of α-Syn aggregates along interconnected neuronal populations within sensory afferents, was concomitant with impaired nociceptive response, reflected by mechanical allodynia, reduced nerve conduction velocities (sensory and motor) and degeneration of small- and medium-sized myelinated fibers. Our findings show a link between the transneuronal propagation of α-Syn pathology with sensory neuron dysfunction and neuropathic impairment, suggesting promising avenues of investigation into the mechanisms underlying pain in PD.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Neuropathic pain; Nociception; Parkinson’s disease; Protein aggregation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Accumulation of alpha-synuclein within the liver, potential role in the clearance of brain pathology associated with Parkinson's disease.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Mar 20;9(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01136-3. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 33743820 Free PMC article.
-
Brain iron enrichment attenuates α-synuclein spreading after injection of preformed fibrils.J Neurochem. 2021 Nov;159(3):554-573. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15461. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 34176164
-
α-Synuclein Induces Progressive Changes in Brain Microstructure and Sensory-Evoked Brain Function That Precedes Locomotor Decline.J Neurosci. 2020 Aug 19;40(34):6649-6659. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0189-20.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32669353 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease and related α-synucleinopathies.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Sep 14;709:134316. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134316. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31170426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain regions susceptible to alpha-synuclein spreading.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Jan;27(1):758-770. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01296-7. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34561613 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Transsynaptic Degeneration in the Aging Brain.Aging Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(5):2149-2167. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.03019. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39191395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of reconfigurable microchannels into aligned three-dimensional neural networks for spatially controllable neuromodulation.Sci Adv. 2023 Mar 10;9(10):eadf0925. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf0925. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 36897938 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Neurodegeneration: Neurovascular Unit in the Spotlight.Cells. 2022 Jun 25;11(13):2023. doi: 10.3390/cells11132023. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipotoxicity Downstream of α-Synuclein Imbalance: A Relevant Pathomechanism in Synucleinopathies?Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 28;12(1):40. doi: 10.3390/biom12010040. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 35053188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloids as Building Blocks for Macroscopic Functional Materials: Designs, Applications and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10698. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910698. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelmotilib H, Maltbie T, Delic V, Liu Z, Hu X, Fraser KB, Moehle MS, Stoyka L, Anabtawi N, Krendelchtchikova V, et al. alpha-Synuclein fibril-induced inclusion spread in rats and mice correlates with dopaminergic Neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;105:84–98. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.05.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bala U, Leong MP, Lim CL, Shahar HK, Othman F, Lai MI, Law ZK, Ramli K, Htwe O, Ling KH, et al. Defects in nerve conduction velocity and different muscle fibre-type specificity contribute to muscle weakness in Ts1Cje Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0197711. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197711. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

