Current Challenges Associated with the Use of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Organoids in Regenerative Medicine
- PMID: 33632980
- PMCID: PMC7904522
- DOI: 10.15283/ijsc20140
Current Challenges Associated with the Use of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Organoids in Regenerative Medicine
Abstract
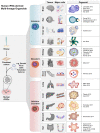
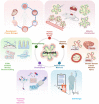
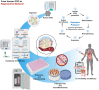
Innovative advances in stem cell research have resulted in the development of organoids, which are widely used as in vitro models of human organ development and for disease. The long-term goals of scientists include the generation of high-quality organoids with properties like those of native organs, and to expand their use to a variety of applications such as drug discovery and organoid-based cell therapy. In particular, the combination of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived organoids with the recently developed genome engineering, biotechnology serve as an attractive platform in precision medicine. This review briefly summarizes the generation of organoids derived mostly from iPSCs without ethical issues, and describes the applications and technological advances of organoids under their differentiation and culture conditions. We also discuss the approaches to improve the organoid models, and how organoids can recapitulate mature organ systems of the human body for regenerative medicine. Finally, the future perspectives and remaining challenges in the field have been discussed to provide a better understanding of the potential applications of organoids.
Keywords: Application; Induced pluripotent stem cell; Organoid; Regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Merits and challenges of iPSC-derived organoids for clinical applications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 26;11:1188905. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1188905. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37305682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Development and Application of Human Organoids: Techniques, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Cell Transplant. 2025 Jan-Dec;34:9636897241303271. doi: 10.1177/09636897241303271. Cell Transplant. 2025. PMID: 39874083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Generation of In Vitro Cardiac Organoids.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 26;24(7):6244. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076244. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges for the Applications of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Liver Organoids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 1;9:748576. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.748576. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34660606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of expandable human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like liver organoids.J Hepatol. 2019 Nov;71(5):970-985. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.030. Epub 2019 Jul 9. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31299272
Cited by
-
Polarization of organoids by bioengineered symmetry breaking.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 May 21;17:22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.05.002. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38881849 Free PMC article.
-
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Alveolar Epithelial Cells as a Tool to Assess Cytotoxicity of Particulate Matter and Cigarette Smoke Extract.Dev Reprod. 2022 Dec;26(4):155-163. doi: 10.12717/DR.2022.26.4.155. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Dev Reprod. 2022. PMID: 36817355 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for Packaging, Transport, and Storage of Source Cells for Organoids.Int J Stem Cells. 2024 May 30;17(2):113-119. doi: 10.15283/ijsc24042. Epub 2024 May 13. Int J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 38735854 Free PMC article.
-
Osteochondral organoids: current advances, applications, and upcoming challenges.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jun 21;15(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03790-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38902814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral Neuron-Organoid Interaction Induces Colonic Epithelial Differentiation via Non-Synaptic Substance P Secretion.Int J Stem Cells. 2023 Aug 30;16(3):269-280. doi: 10.15283/ijsc23026. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Int J Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 37385635 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

