Drug Discovery Insights from Medicinal Beetles in Traditional Chinese Medicine
- PMID: 33632986
- PMCID: PMC7921859
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.229
Drug Discovery Insights from Medicinal Beetles in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Abstract
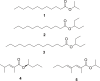
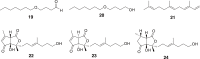
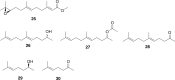
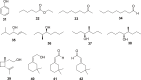
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) was the primary source of medical treatment for the people inhabiting East Asia for thousands of years. These ancient practices have incorporated a wide variety of materia medica including plants, animals and minerals. As modern sciences, including natural products chemistry, emerged, there became increasing efforts to explore the chemistry of this materia medica to find molecules responsible for their traditional use. Insects, including beetles have played an important role in TCM. In our survey of texts and review articles on TCM materia medica, we found 48 species of beetles from 34 genera in 14 different families that are used in TCM. This review covers the chemistry known from the beetles used in TCM, or in cases where a species used in these practices has not been chemically studied, we discuss the chemistry of closely related beetles. We also found several documented uses of beetles in Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM), and included them where appropriate. There are 129 chemical constituents of beetles discussed.
Keywords: Beetle; Chemical defense; Coleoptera; Secondary metabolites; Traditional Chinese Medicine; Traditional Korean Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures













References
-
- Allison J. D., Borden J. H., Seybold S. J. A review of the chemical ecology of the Cerambycidae (Coleoptera) Chemoecology. 2004;14:123–150. doi: 10.1007/s00049-004-0277-1. - DOI
-
- Altson A. M. On the genital system of Lyctus brunneus Steph., with a note on Lyctus linearis Goeze (Coleoptera) Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1924;35:581–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-3642.1924.tb00056.x. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

