Cohnella 1759 cysteine protease shows significant long term half-life and impressive increased activity in presence of some chemical reagents
- PMID: 33633359
- PMCID: PMC7907070
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84267-w
Cohnella 1759 cysteine protease shows significant long term half-life and impressive increased activity in presence of some chemical reagents
Abstract
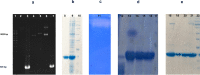
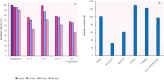
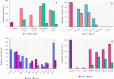
Thermostability and substrate specificity of proteases are major factors in their industrial applications. rEla is a novel recombinant cysteine protease obtained from a thermophilic bacterium, Cohnella sp.A01 (PTCC No: 1921). Herein, we were interested in recombinant production and characterization of the enzyme and finding the novel features in comparison with other well-studied cysteine proteases. The bioinformatics analysis showed that rEla is allosteric cysteine protease from DJ-1/ThiJ/PfpI superfamily. The enzyme was heterologously expressed and characterized and the recombinant enzyme molecular mass was 19.38 kD which seems to be smaller than most of the cysteine proteases. rEla exhibited acceptable activity in broad pH and temperature ranges. The optimum activity was observed at 50℃ and pH 8 and the enzyme showed remarkable stability by keeping 50% of residual activity after 100 days storage at room temperature. The enzyme Km and Vmax values were 21.93 mM, 8 U/ml, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, in comparison with the other characterized cysteine proteases, rEla is the only reported cysteine protease with collagen specificity. The enzymes activity increases up to 1.4 times in the presence of calcium ion (2 mM) suggesting it as the enzyme's co-factor. When exposed to surfactants including Tween20, Tween80, Triton X-100 and SDS (1% and 4% v/v) the enzyme activity surprisingly increased up to 5 times.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structural and biochemical characterization of a novel thermophilic Coh01147 protease.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 23;15(6):e0234958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234958. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32574185 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous expression, purification, and biochemical characterization of protease 3075 from Cohnella sp. A01.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 16;19(12):e0310910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310910. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39680596 Free PMC article.
-
Novel halo- and thermo-tolerant Cohnella sp. A01 L-glutaminase: heterologous expression and biochemical characterization.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 13;9(1):19062. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55587-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31836796 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine Protease Zymography: Brief Review.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1626:25-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7111-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28608197 Review.
-
Cysteine cathepsins: from structure, function and regulation to new frontiers.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1824(1):68-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22024571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and functional characterization of safflower cysteine protease 1 as negative regulator in response to low-temperature stress in transgenic Arabidopsis.Planta. 2022 Apr 21;255(5):106. doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-03875-6. Planta. 2022. PMID: 35445865
-
Endo-xylanases from Cohnella sp. AR92 aimed at xylan and arabinoxylan conversion into value-added products.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;105(18):6759-6778. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11495-5. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34458936
-
Characterization of high-yield Bacillus subtilis cysteine protease for diverse industrial applications.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Jun;54(2):739-752. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-00992-6. Epub 2023 May 9. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37157054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vincents B, Pawel-rammingen UV, Bjo L. Enzymatic characterization of the streptococcal endopeptidase, IdeS, reveals that it is a cysteine protease with strict specificity for IgG cleavage due to exosite. Biomolecules. 2004;1:15540–15549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

