Role of percutaneous vertebroplasty with high-viscosity cement in the treatment of severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
- PMID: 33633366
- PMCID: PMC7907187
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84314-6
Role of percutaneous vertebroplasty with high-viscosity cement in the treatment of severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Abstract
Severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) were considered as relative or even absolute contraindication for vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty and these relevant reports are very limited. This study aimed to evaluate and compare the efficacy of vertebroplasty with high-viscosity cement and conventional kyphoplasty in managing severe OVCFs. 37 patients of severe OVCFs experiencing vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty were reviewed and divided into two groups, according to the procedural technique, 18 in high-viscosity cement percutaneous vertebroplasty (hPVP) group and 19 in conventional percutaneous kyphoplasty (cPKP) group. The operative time, and injected bone cement volume were recorded. Anterior vertebral height (AVH), Cobb angle and cement leakage were also evaluated in the radiograph. The rate of cement leakage was lower in hPVP group, compared with cPKP group (16.7% vs 47.4%, P = 0.046). The patients in cPKP group achieved more improvement in AVH and Cobb angle than those in hPVP group postoperatively (37.2 ± 7.9% vs 43.0 ± 8.9% for AVH, P = 0.044; 15.5 ± 4.7 vs 12.7 ± 3.3, for Cobb angle, P = 0.042). At one year postoperatively, there was difference observed in AVH between two groups (34.1 ± 7.4 vs 40.5 ± 8.7 for hPVP and cPKP groups, P = 0.021), but no difference was found in Cobb angle (16.6 ± 5.0 vs 13.8 ± 3.8, P = 0.068). Similar cement volume was injected in two groups (2.9 ± 0.5 ml vs 2.8 ± 0.6 ml, P = 0.511). However, the operative time was 37.8 ± 6.8 min in the hPVP group, which was shorter than that in the cPKP group (43.8 ± 8.2 min, P = 0.021). In conclusion, conventional PKP achieved better in restoring anterior vertebral height and improving kyphotic angle, but PVP with high-viscosity cement had lower rate of cement leakage and shorter operative time with similar volume of injected cement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
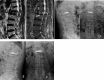
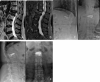
References
-
- Chen X, et al. Is unilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty superior to bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures? Evidence from a systematic review of discordant meta-analyses. Pain Physician. 2018;21:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Fuentes, S. et al. Open kyphoplasty for management of severe osteoporotic spinal fractures. Neurosurgery64, 350–354; discussion 354–355 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Nieuwenhuijse, M. J., van Erkel, A. R. & Dijkstra, P. D. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: feasible and beneficial. J. Vasc. Intervent. Radiol.: JVIR22, 1017–1023 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

