Treatment Satisfaction, Patient Preferences, and the Impact of Suboptimal Disease Control in a Large International Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort: SENSE Study
- PMID: 33633444
- PMCID: PMC7900444
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S289692
Treatment Satisfaction, Patient Preferences, and the Impact of Suboptimal Disease Control in a Large International Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort: SENSE Study
Abstract
Background: Patients' needs and perspectives are important determinants of treatment success in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Assessing patients' perspectives can help identify unmet needs and enhance the understanding of treatment benefits.
Objective: The SENSE study assessed the impact of inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) on treatment satisfaction, disease outcomes, and patient perspectives related to RA disease management.
Methods: SENSE was a noninterventional, cross-sectional study conducted in 18 countries across Europe, Asia, and South America. Adult patients with poorly controlled RA of moderate/high disease activity were eligible. Patient satisfaction was assessed by the Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM v1.4). Treatment adherence, healthcare resource utilization (HRU), quality of life (QoL), work ability, digital health literacy (DHL), patient preference information, and treatment strategy were also assessed.
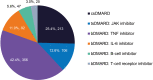
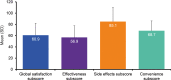
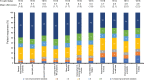
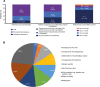
Results: A total of 1624 patients were included in the study: most were female (84.2%) and middle-aged, and mean disease duration was 10.5 years. Mean TSQM global satisfaction subscore was 60.9, with only 13.5% of patients reporting good treatment satisfaction (TSQM global ≥80). The strongest predictor of good treatment satisfaction was treatment with advanced therapies. Most patients (87.4%) reported good treatment adherence. In general, patients had impaired QoL and work ability, high HRU, and 67.4% had poor DHL. Leading treatment expectations were "general improvement of arthritis" and "less joint pain". Most patients preferred oral RA medications (60.7%) and rapid (≤1 week) onset of action (71.1%). "Increased risk for malignancies" and "increased risk for cardiovascular disease" were the least acceptable side effects. Despite suboptimal control, advanced therapies were only used in a minority of patients, and DMARD switches were planned for only half of the patients.
Conclusion: Suboptimal disease control negatively impacts treatment satisfaction, work ability, QoL, and HRU. Data collected on patient perspectives may inform shared decision-making and optimize treat-to-target strategies for improving patient outcomes in RA.
Keywords: adherence; digital health literacy; patient preference; rheumatoid arthritis; treatment satisfaction.
© 2021 Taylor et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Peter C. Taylor received research grants, consultation, and/or speaking fees from AbbVie, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Fresenius, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; Codrina Ancuta received consultation and/or speaker fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Ewopharma, Merck Sharpe and Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; Andrey Gordeev received speaker fees from AbbVie; Radka Janková received speaker fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharpe and Dohme, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and UCB; Umut Kalyoncu received consultation and/or speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; Jadranka Morović-Vergles received speaker fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Ewopharma, Merck Sharpe and Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; Mariana Peixoto G. U. e Silva de Souza received research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GSK, Pfizer, and UCB; honoraria for consultancies and/or speaking engagements from AbbVie, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; and is a Member of RA commission – Brazilian Society of Rheumatology and vice-president of SMR (Regional Society of Rheumatology); Prodromos Sidiropoulos received research grants, consultation, and/or speaking fees from AbbVie, Amgen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; Atsushi Kawakami received speaker fees from AbbVie GK., Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan Ltd., Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation., Astellas Pharma Inc, Celltrion Healthcare Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Eisai Co., Eli Lilly Japan, GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Kowa Co., Ltd., MedPeer Inc, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Novartis Pharma Inc, ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Taisho Pharma Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Pfizer Japan Inc; and grants and research support from AbbVie GK., Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan Ltd., Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, Astellas Pharma Inc, AYUMI Pharmaceutical Co., Boehringer Ingelheim Japan, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion Healthcare Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Eisai Co., Eli Lilly Japan, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., MSD K.K., Neopharma Japan Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma Inc, ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Sanofi K.K., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Science Foundation, and Teijin Pharma Co. Orsolya Nagy and Ivan Lagunes-Galindo are employees of AbbVie and may own stock or options in AbbVie. No relevant conflicts of interest were declared by María C. de la Vega and Bernadette Rojkovich. The authors report no other conflicts of interest related to this work. Some of the data from this paper were presented at the EULAR 2020 Congress as a poster presentation (SAT0123). The poster’s abstract was published in the “Scientific Abstracts” section in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases (Taylor et al Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79:996–997; https://ard.bmj.com/content/79/Suppl_1/996).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment Satisfaction, Patient Preferences, and the Impact of Suboptimal Disease Control in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Greece: Analysis of the Greek Cohort of SENSE study.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022 Mar 31;33(1):14-34. doi: 10.31138/mjr.33.1.14. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35611113 Free PMC article.
-
Patient satisfaction, preferences, expectations, characteristics, and impact of suboptimal control of rheumatoid arthritis: A subgroup analysis of Japanese patients from a large international cohort study (SENSE).PLoS One. 2021 Nov 15;16(11):e0259389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259389. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34780502 Free PMC article.
-
The perspective of Polish patients with rheumatoid arthritis - treatment expectations, patient-reported outcomes, and digital literacy (the SENSE study).Reumatologia. 2023;61(5):331-338. doi: 10.5114/reum/171625. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Reumatologia. 2023. PMID: 37970121 Free PMC article.
-
Patient Preferences for Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drug Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review.J Rheumatol. 2020 Feb;47(2):176-187. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.181165. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 30988125
-
Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Older Adults and Elderly Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Role Can Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs Play in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction?Drugs Aging. 2019 Jun;36(6):493-510. doi: 10.1007/s40266-019-00653-0. Drugs Aging. 2019. PMID: 30953327 Review.
Cited by
-
Treat-to-target in rheumatoid arthritis: a real-world study of the application and impact of treat-to-target within the wider context of patient management, patient centricity and advanced therapy use in Europe.RMD Open. 2022 Dec;8(2):e002658. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002658. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 36549856 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Satisfaction, Patient Preferences, and the Impact of Suboptimal Disease Control in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Greece: Analysis of the Greek Cohort of SENSE study.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022 Mar 31;33(1):14-34. doi: 10.31138/mjr.33.1.14. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35611113 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived treatment satisfaction in patients with systemic rheumatic diseases treated with biologic therapies: results of a self-reported survey.Rheumatol Int. 2023 Jun;43(6):1151-1159. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05280-y. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Rheumatol Int. 2023. PMID: 36786872 Free PMC article.
-
Questionnaire Survey of Japanese Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Physicians on Shared Decision-Making in Advanced Therapy: A Web-Based PAIR Survey.Crohns Colitis 360. 2025 Apr 9;7(2):otaf014. doi: 10.1093/crocol/otaf014. eCollection 2025 Apr. Crohns Colitis 360. 2025. PMID: 40343010 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to, Facilitators of, and Interventions to Support Treat-to-Target Implementation in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024 Dec;76(12):1626-1636. doi: 10.1002/acr.25408. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39090845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FDA guidance: guidance on patient preference information in premarket approval applications, humanitarian device exemption applications, and de novo requests. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/medicaldevices/deviceregulationandguidance/.... Accessed August24, 2016
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

