The Cost-Effectiveness of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Versus Open Reduction Internal Fixation for Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Elderly
- PMID: 33633504
- PMCID: PMC7894060
The Cost-Effectiveness of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Versus Open Reduction Internal Fixation for Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Elderly
Abstract
Background: Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of proximal humerus fractures in elderly individuals (age >70) carries a relatively high short-term complication and reoperation rate but is generally durable once healed. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) for fractures may be associated with superior short-term quality of life but carries the lifelong liabilities of joint replacement. The tradeoff between short and long-term risks, coupled with disparities in quality of life and cost, makes this clinical decision amenable to cost-effectiveness analysis.
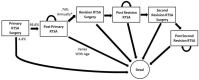
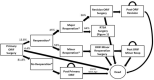
Methods: A Markov state-transition model was constructed with a base case of a 75 year-old patient. Reoperation rates, quality of life values, mortality rates, and costs were based upon published literature. The model was run until all patients had died to simulate the accumulated costs and benefits.
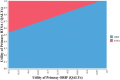
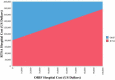
Results: RTSA was associated with greater quality of life (7.11 QALYs) than ORIF (6.22 QALYs). RTSA was cost-effective with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $3,945/QALY and $27,299/ QALY from payor and hospital perspectives, respectively. RTSA was favored and cost-effective at any age above 65 and any Charlson Score. The model was sensitive to the utility of both procedures.
Conclusion: RTSA resulted in a higher quality of life and was cost-effective in comparison to ORIF for elderly patients.Level of Evidence: III.
Keywords: cost-effectiveness; open reduction and internal fixation; proximal humerus fracture; reverse total shoulder arthroplasty.
Copyright © The Iowa Orthopaedic Journal 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors report no potential conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Baron JA, Barrett J, Karagas M. The epidemiology of peripheral fractures. Bone. 1996;18(3):S209–S13. - PubMed
-
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37(8):691–7. - PubMed
-
- Court-Brown CM, Garg A, McQueen MM. The epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Acta orthopaedica Scandinavica. 2001;72(4):365–71. Epub 2001/10/03. - PubMed
-
- Owsley KC, Gorczyca JT. Displacement/screw cutout after open reduction and locked plate fixation of humeral fractures. JBJS. 2008;90(2):233–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
