Enhanced Healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans Treated With Extracts From the Traditional Chinese Medicine Plants Cuscuta chinensis Lam. and Eucommia ulmoides Oliv
- PMID: 33633573
- PMCID: PMC7901915
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.604435
Enhanced Healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans Treated With Extracts From the Traditional Chinese Medicine Plants Cuscuta chinensis Lam. and Eucommia ulmoides Oliv
Abstract
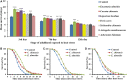
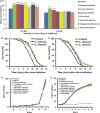
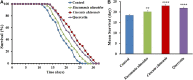
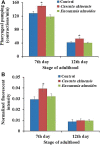
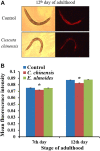
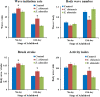
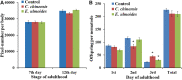
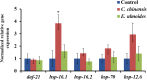
To uncover potential anti-aging capacities of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans was used to investigate the effects of Eucommia ulmoides and Cuscuta chinensis extracts, selected by screening seven TCM extracts, on different healthspan parameters. Nematodes exposed to E. ulmoides and C. chinensis extracts, starting at the young adult stage, exhibited prolonged lifespan and increased survival after heat stress as well as upon exposure to the pathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens, whereby the survival benefits were monitored after stress initiation at different adult stages. However, only C. chinensis had the ability to enhance physical fitness: the swimming behavior and the pharyngeal pumping rate of C. elegans were improved at day 7 and especially at day 12 of adulthood. Finally, monitoring the red fluorescence of aged worms revealed that only C. chinensis extracts caused suppression of intestinal autofluorescence, a known marker of aging. The results underline the different modes of action of the tested plants extracts. E. ulmoides improved specifically the physiological fitness by increasing the survival probability of C. elegans after stress, while C. chinensis seems to be an overall healthspan enhancer, reflected in the suppressed autofluorescence, with beneficial effects on physical as well as physiological fitness. The C. chinensis effects may be hormetic: this is supported by increased gene expression of hsp-16.1 and by trend, also of hsp-12.6.
Keywords: C. elegans; Cuscuta chinensis; Eucommia ulmoides; aging; healthspan; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2021 Sayed, Siems, Schmitz-Linneweber, Luyten and Saul.
Conflict of interest statement
Author KS was employed by the company AnalytiCon Discovery GmbH, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a Hydroxygallic Acid Derivative, Zingibroside R1 and a Sterol Lipid as Potential Active Ingredients of Cuscuta chinensis Extract That Has Neuroprotective and Antioxidant Effects in Aged Caenorhabditis elegans.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 9;14(19):4199. doi: 10.3390/nu14194199. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235851 Free PMC article.
-
Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):78-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24296089 Review.
-
Extract from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. ameliorates arthritis via regulation of inflammation, synoviocyte proliferation and osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 24;194:609-616. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.038. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27743778
-
Eucommia ulmoides male flower as a remarkable edible floral resource exerts lifespan/healthspan-promoting effects on Caenorhabditis elegans.Food Funct. 2023 Jan 3;14(1):457-470. doi: 10.1039/d2fo03006c. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 36519399
-
Traditional application and modern pharmacological research of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.Chin Med. 2021 Aug 6;16(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00482-7. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34362420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Impact of Onobrychis cornuta and Veratrum lobelianum Extracts on C. elegans: Implications for MAPK Modulation, Germline Development, and Antitumor Properties.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 19;16(1):8. doi: 10.3390/nu16010008. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38201838 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Hydroxygallic Acid Derivative, Zingibroside R1 and a Sterol Lipid as Potential Active Ingredients of Cuscuta chinensis Extract That Has Neuroprotective and Antioxidant Effects in Aged Caenorhabditis elegans.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 9;14(19):4199. doi: 10.3390/nu14194199. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235851 Free PMC article.
-
Torenia sp. Extracts Contain Multiple Potent Antitumor Compounds with Nematocidal Activity, Triggering an Activated DNA Damage Checkpoint and Defective Meiotic Progression.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 10;17(5):611. doi: 10.3390/ph17050611. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794181 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal Extract-Induced DNA Damage, Apoptosis, and Antioxidant Effects of C. elegans: A Comparative Study of Mentha longifolia, Scrophularia orientalis, and Echium biebersteinii.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;18(7):1030. doi: 10.3390/ph18071030. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732318 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Macroporous Resin for Green Recovery of Iridoids, Chlorogenic Acid, and Flavonoids from Eucommia ulmoides Leaves.Molecules. 2024 Feb 5;29(3):737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balasubramaniam B., Vinitha T., Deepika S., Jebamercy G., Venkatakrishna L. M., Balamurugan K. (2019). Analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans phosphoproteome reveals the involvement of a molecular chaperone, HSP-90 protein during Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 137, 620–646. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.085 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Büchter C., Zhao L., Havermann S., Honnen S., Fritz G., Proksch P., et al. (2015). TSG (2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside) from the Chinese herb polygonum multiflorum increases life span and stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans . Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 124357 10.1155/2015/124357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

