Enhanced Healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans Treated With Extracts From the Traditional Chinese Medicine Plants Cuscuta chinensis Lam. and Eucommia ulmoides Oliv
- PMID: 33633573
- PMCID: PMC7901915
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.604435
Enhanced Healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans Treated With Extracts From the Traditional Chinese Medicine Plants Cuscuta chinensis Lam. and Eucommia ulmoides Oliv
Abstract
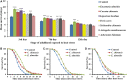
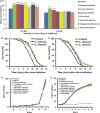
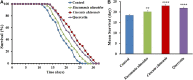
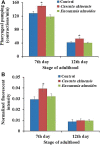
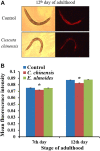
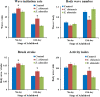
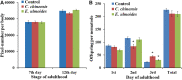
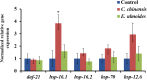
To uncover potential anti-aging capacities of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans was used to investigate the effects of Eucommia ulmoides and Cuscuta chinensis extracts, selected by screening seven TCM extracts, on different healthspan parameters. Nematodes exposed to E. ulmoides and C. chinensis extracts, starting at the young adult stage, exhibited prolonged lifespan and increased survival after heat stress as well as upon exposure to the pathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens, whereby the survival benefits were monitored after stress initiation at different adult stages. However, only C. chinensis had the ability to enhance physical fitness: the swimming behavior and the pharyngeal pumping rate of C. elegans were improved at day 7 and especially at day 12 of adulthood. Finally, monitoring the red fluorescence of aged worms revealed that only C. chinensis extracts caused suppression of intestinal autofluorescence, a known marker of aging. The results underline the different modes of action of the tested plants extracts. E. ulmoides improved specifically the physiological fitness by increasing the survival probability of C. elegans after stress, while C. chinensis seems to be an overall healthspan enhancer, reflected in the suppressed autofluorescence, with beneficial effects on physical as well as physiological fitness. The C. chinensis effects may be hormetic: this is supported by increased gene expression of hsp-16.1 and by trend, also of hsp-12.6.
Keywords: C. elegans; Cuscuta chinensis; Eucommia ulmoides; aging; healthspan; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2021 Sayed, Siems, Schmitz-Linneweber, Luyten and Saul.
Conflict of interest statement
Author KS was employed by the company AnalytiCon Discovery GmbH, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Balasubramaniam B., Vinitha T., Deepika S., Jebamercy G., Venkatakrishna L. M., Balamurugan K. (2019). Analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans phosphoproteome reveals the involvement of a molecular chaperone, HSP-90 protein during Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 137, 620–646. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.085 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Büchter C., Zhao L., Havermann S., Honnen S., Fritz G., Proksch P., et al. (2015). TSG (2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside) from the Chinese herb polygonum multiflorum increases life span and stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans . Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 124357 10.1155/2015/124357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

