Antinociceptive Effects of Sinomenine Combined With Ligustrazine or Paracetamol in Animal Models of Incisional and Inflammatory Pain
- PMID: 33633575
- PMCID: PMC7900506
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.523769
Antinociceptive Effects of Sinomenine Combined With Ligustrazine or Paracetamol in Animal Models of Incisional and Inflammatory Pain
Abstract
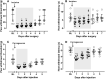
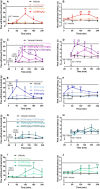
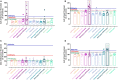
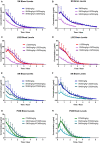
The management of postoperative and inflammatory pain has been a pressing challenge in clinical settings. Sinomenine (SN) is a morphinan derived alkaloid with remarkable analgesic properties in various kinds of pain models. The aim of the current study is to investigate if SN can enhance the effect of ligustrazine hydrochloride (LGZ) or paracetamol (PCM) in animal models of postoperative and inflammatory pain. And to determine if the combined therapeutic efficacies can be explained by pharmacokinetics changes. Pharmacological studies were performed using a rat model of incisional pain, and a mouse model of carrageenan induced inflammatory pain. Pharmacokinetic studies were performed using a microdialysis sampling and HPLC-MS/MS assay method to quantify SN, LGZ, and PCM levels in blood and extracellular fluid in brain. We found that SN plus LGZ or SN plus PCM produced marked synergistic analgesic effects. However, such synergy was subjected to pain modalities, and differed among pain models. Pharmacological discoveries could be partially linked to pharmacokinetic alterations in SN combinations. Though further evaluation is needed, our findings advocate the potential benefits of SN plus LGZ for postoperative pain management, and SN plus PCM for controlling inflammatory pain.
Keywords: carrageenan-induced inflammation; drug combinations; microdialysis; neuroimmune interaction; pharmacokinetics; post-operative pain.
Copyright © 2021 Gao, Li, Jiang, Fan, Xu, Zhao, Yin, Guo, Wang, Gao, Han, Jiang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
WJ and WF were employed by the company Zhejiang Zhenyuan Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using Integrated Network Pharmacology and Metabolomics to Reveal the Mechanisms of the Combined Intervention of Ligustrazine and Sinomenine in CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 13;26(6):2604. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062604. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141247 Free PMC article.
-
Sinomenine facilitates the efficacy of gabapentin or ligustrazine hydrochloride in animal models of neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 5;854:101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.061. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30954565
-
Exploratory study data for determining the adverse effects of sinomenine plus gabapentin or ligustrazine hydrochloride and the pharmacokinetic insights of sinomenine in plasma and CNS tissue.Data Brief. 2019 Oct 8;27:104633. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2019.104633. eCollection 2019 Dec. Data Brief. 2019. PMID: 31667325 Free PMC article.
-
Combination analgesia in 2005 - a rational approach: focus on paracetamol-tramadol.Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25 Suppl 1:S16-21. doi: 10.1007/s10067-006-0202-9. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Clin Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16741784 Review.
-
Analgesic Mechanism of Sinomenine against Chronic Pain.Pain Res Manag. 2020 May 6;2020:1876862. doi: 10.1155/2020/1876862. eCollection 2020. Pain Res Manag. 2020. PMID: 32454918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analgesic Alkaloids Derived From Traditional Chinese Medicine in Pain Management.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 10;13:851508. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.851508. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35620295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential therapeutic effects and pharmacological evidence of sinomenine in central nervous system disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 16;13:1015035. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015035. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of benidipine, paracetamol, and their combination on postoperative and normal tissue pain thresholds.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 5;14:1326128. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1326128. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38249347 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2 Receptor Activation Blocks GluA2/ROS Positive Feedback Loop to Alienate Chronic-Migraine-Associated Pain Sensitization.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;13(6):725. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060725. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929165 Free PMC article.
-
Dexborneol Amplifies Pregabalin's Analgesic Effect in Mouse Models of Peripheral Nerve Injury and Incisional Pain.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;13(7):803. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070803. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061872 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

