Rhizobium leguminosarum Glutathione Peroxidase Is Essential for Oxidative Stress Resistance and Efficient Nodulation
- PMID: 33633710
- PMCID: PMC7900000
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.627562
Rhizobium leguminosarum Glutathione Peroxidase Is Essential for Oxidative Stress Resistance and Efficient Nodulation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Rhizobium leguminosarum Glutathione Peroxidase Is Essential for Oxidative Stress Resistance and Efficient Nodulation.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 15;12:789870. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.789870. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34975812 Free PMC article.
Abstract
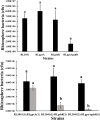
Glutathione (GSH) plays a key role in regulating the cellular Redox Homeostasis, and appears to be essential for initiation and development of root nodules. Glutathione peroxidase (Gpx) catalyzes the reduction of H2O2 and organic hydroperoxides by oxidation of GSH to oxidized GSH (GSSG), which in turn is reduced by glutathione reductase (GR). However, it has not been determined whether the Rhizobium leguminosarum Gpx or GR is required during symbiotic interactions with pea. To characterize the role of glutathione-dependent enzymes in the symbiotic process, single and double mutants were made in gpxA (encoding glutathione peroxidase) and gshR (encoding glutathione reductase) genes. All the mutations did not affect the rhizobial growth, but they increased the sensitivity of R. leguminosarum strains to H2O2. Mutant in GpxA had no effect on intracellular GSH levels, but can increase the expression of the catalase genes. The gshR mutant can induce the formation of normal nodules, while the gpxA single and double mutants exhibited a nodulation phenotype coupled to more than 50% reduction in the nitrogen fixation capacity, these defects in nodulation were characterized by the formation of ineffective nodules. In addition, the gpxA and gshR double mutant was severely impaired in rhizosphere colonization and competition. Quantitative proteomics using the TMT labeling method was applied to study the differential expression of proteins in bacteroids isolated from pea root nodules. A total of 27 differentially expressed proteins were identified in these root bacteroids including twenty down-regulated and seven up-regulated proteins. By sorting the down-regulated proteins, eight are transporter proteins, seven are dehydrogenase, deoxygenase, oxidase, and hydrolase. Moreover, three down-regulating proteins are directly involved in nodule process.
Keywords: Rhizobium leguminosarum; antioxidant function; glutathione peroxidase; quantitative proteomics; symbiotic nitrogen fixation.
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Chen, Luo, Zou, Xie, He, Li and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
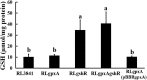

Similar articles
-
A GMC Oxidoreductase GmcA Is Required for Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae.Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 24;11:394. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00394. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32265862 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant ability of glutaredoxins and their role in symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae 3841.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Mar 1;87(4):e01956-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01956-20. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33277272 Free PMC article.
-
Sinorhizobium meliloti Glutathione Reductase Is Required for both Redox Homeostasis and Symbiosis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jan 17;84(3):e01937-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01937-17. Print 2018 Feb 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29150514 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione affects the transport activity of Rhizobium leguminosarum 3841 and is essential for efficient nodulation.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017 Apr 1;364(8):fnx045. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnx045. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28333211 Free PMC article.
-
Genes involved in the formation and assembly of rhizobial cytochromes and their role in symbiotic nitrogen fixation.Adv Microb Physiol. 1998;40:191-231. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60132-0. Adv Microb Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9889979 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Face of the Old Gene: Deletion of the PssA, Encoding Monotopic Inner Membrane Phosphoglycosyl Transferase in Rhizobium leguminosarum, Leads to Diverse Phenotypes That Could Be Attributable to Downstream Effects of the Lack of Exopolysaccharide.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1035. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021035. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674551 Free PMC article.
-
Callose metabolism and the regulation of cell walls and plasmodesmata during plant mutualistic and pathogenic interactions.Plant Cell Environ. 2023 Feb;46(2):391-404. doi: 10.1111/pce.14510. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Plant Cell Environ. 2023. PMID: 36478232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taxonomic Identification of the Arctic Strain Nocardioides Arcticus Sp. Nov. and Global Transcriptomic Analysis in Response to Hydrogen Peroxide Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 11;24(18):13943. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813943. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762246 Free PMC article.
-
The Mesorhizobium huakuii transcriptional regulator AbiEi plays a critical role in nodulation and is important for bacterial stress response.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Sep 12;21(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02304-0. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34511061 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

