At FUT4 and At FUT6 Are Arabinofuranose-Specific Fucosyltransferases
- PMID: 33633757
- PMCID: PMC7900004
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.589518
At FUT4 and At FUT6 Are Arabinofuranose-Specific Fucosyltransferases
Abstract
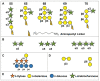
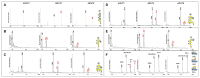
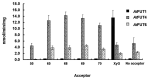
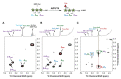
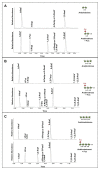
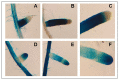
The bulk of plant biomass is comprised of plant cell walls, which are complex polymeric networks, composed of diverse polysaccharides, proteins, polyphenolics, and hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs). Glycosyltransferases (GTs) work together to synthesize the saccharide components of the plant cell wall. The Arabidopsis thaliana fucosyltransferases (FUTs), AtFUT4, and AtFUT6, are members of the plant-specific GT family 37 (GT37). AtFUT4 and AtFUT6 transfer fucose (Fuc) onto arabinose (Ara) residues of arabinogalactan (AG) proteins (AGPs) and have been postulated to be non-redundant AGP-specific FUTs. AtFUT4 and AtFUT6 were recombinantly expressed in mammalian HEK293 cells and purified for biochemical analysis. We report an updated understanding on the specificities of AtFUT4 and AtFUT6 that are involved in the synthesis of wall localized AGPs. Our findings suggest that they are selective enzymes that can utilize various arabinogalactan (AG)-like and non-AG-like oligosaccharide acceptors, and only require a free, terminal arabinofuranose. We also report with GUS promoter-reporter gene studies that AtFUT4 and AtFUT6 gene expression is sub-localized in different parts of developing A. thaliana roots.
Keywords: AtFUT1; AtFUT4; AtFUT6; Fucosyltransferase; GT37; arabinogalactan protein; hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein; plant cell wall.
Copyright © 2021 Soto, Prabhakar, Wang, Backe, Chapla, Bartetzko, Black, Azadi, Peña, Pfrengle, Moremen, Urbanowicz and Hahn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bonin C. P., Potter I., Vanzin G. F., Reiter W. D. (1997). The MUR1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes an isoform of GDP-d-mannose-4,6-dehydratase, catalyzing the first step in the de novo synthesis of GDP-l-fucose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 2085–2090. 10.1073/PNAS.94.5.2085, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

