Screening of Onion (Allium cepa L.) Genotypes for Drought Tolerance Using Physiological and Yield Based Indices Through Multivariate Analysis
- PMID: 33633759
- PMCID: PMC7900547
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.600371
Screening of Onion (Allium cepa L.) Genotypes for Drought Tolerance Using Physiological and Yield Based Indices Through Multivariate Analysis
Abstract
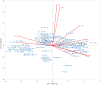
Drought is a leading abiotic constraints for onion production globally. Breeding by using unique genetic resources for drought tolerance is a vital mitigation strategy. With a total of 100 onion genotypes were screened for drought tolerance using multivariate analysis. The experiment was conducted in a controlled rainout shelter for 2 years 2017-2018 and 2018-2019 in a randomized block design with three replications and two treatments (control and drought stress). The plant was exposed to drought stress during the bulb development stage (i.e., 50-75 days after transplanting). The genotypes were screened on the basis of the drought tolerance efficiency (DTE), percent bulb yield reduction, and results of multivariate analysis viz. hierarchical cluster analysis by Ward's method, discriminate analysis and principal component analysis. The analysis of variance indicated significant differences among the tested genotypes and treatments for all the parameters studied, viz. phenotypic, physiological, biochemical, and yield attributes. Bulb yield was strongly positively correlated with membrane stability index (MSI), relative water content (RWC), total chlorophyll content, antioxidant enzyme activity, and leaf area under drought stress. The genotypes were categorized into five groups namely, highly tolerant, tolerant, intermediate, sensitive, and highly sensitive based on genetic distance. Under drought conditions, clusters II and IV contained highly tolerant and highly sensitive genotypes, respectively. Tolerant genotypes, viz. Acc. 1656, Acc. 1658, W-009, and W-085, had higher DTE (>90%), fewer yield losses (<20%), and performed superiorly for different traits under drought stress. Acc. 1627 and Acc. 1639 were found to be highly drought-sensitive genotypes, with more than 70% yield loss. In biplot, the tolerant genotypes (Acc. 1656, Acc. 1658, W-085, W-009, W-397, W-396, W-414, and W-448) were positively associated with bulb yield, DTE, RWC, MSI, leaf area, and antioxidant enzyme activity under drought stress. The study thus identified tolerant genotypes with favorable adaptive traits that may be useful in onion breeding program for drought tolerance.
Keywords: drought; genetic diversity; multivariate analysis; onion; stress indices.
Copyright © 2021 Gedam, Thangasamy, Shirsat, Ghosh, Bhagat, Sogam, Gupta, Mahajan, Soumia, Salunkhe, Khade, Gawande, Hanjagi, Ramakrishnan and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aghaie P., Tafreshi S. A. H., Ebrahimi M. A., Haerinasab M. (2018). Tolerance evaluation and clustering of fourteen tomato cultivars grown under mild and severe drought conditions. Sci. Hortic. 232 1–12. 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.12.041 - DOI
-
- Ansari W. A., Atri N., Singh B., Pandey S. (2017). Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expression in two muskmelon genotypes under progressive water stress. Biol. Plant. 61 333–341. 10.1007/s10535-016-0694-3 - DOI
-
- Arifuzzaman M., Barman S., Hayder S., Azad M. A. K., Turin M. T. S., Amzad M. A., et al. (2020). Screening of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes under drought stress conditions using multivariate analysis. Cereal Res. Commun. 48 301–308. 10.1007/s42976-020-00039-8 - DOI
-
- Bahrami F., Arzani A., Karimi V. (2014). Evaluation of yield-based drought tolerance indices for screening safflower genotypes. Agron. J. 106 1219–1224. 10.2134/agronj13.0387 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources