Clinical implications of Delphian lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 33633964
- PMCID: PMC7882338
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-20-521
Clinical implications of Delphian lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
Background: As is known, identifying risk factors precisely for lymph node metastasis (LNM) plays a vital role in initial treatment for papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Nonetheless, whether Delphian lymph node (DLN) metastasis has value in predicting LNM remains an open question. This study covered a sample of 1,575 patients, which is the largest sample group so far, aiming to assess the predictive validity of DLN metastasis in PTC.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted with 1,575 eligible PTC patients who underwent thyroid operation between July 2013 and December 2018 and clinicopathologic parameters of patients with DLN metastasis were compared with those without DLN metastasis.
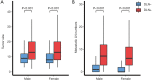
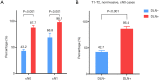
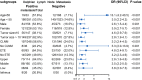
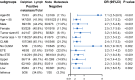
Results: The incidence of DLN metastasis, according to our research samples, is 24.4% (384/1,575 patients). And results show that DLN positivity was closely associated with adverse prognostic factors including younger age, larger tumor size, extrathyroid extension, tumor location in the isthmus or upper lobe of the thyroid, number of LNM >5, higher recurrence. After carefully adjusting important confounding factors, we find that in multivariate logistic regression analyses, DLN metastasis is an independent predictor for both central LNM (CLNM, adjusted OR =7.81, P<0.001) and lateral LNM (LLNM, adjusted OR =3.40, P<0.001). Moreover, the stratified analyses also show convincing evidence of a positive correlation between DLN metastasis and LNM in levels II-IV in the vast majority of subgroups.
Conclusions: The present study suggests that DLN metastasis is an independent risk factor for CLNM and LLNM of levels II-IV. The cervical lymph nodes should be meticulously evaluated to guide tailored treatment during operation in patients with DLN involvement.
Keywords: Delphian lymph nodes metastasis; Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC); central lymph node metastasis (CLNM); lateral lymph node metastasis (LLNM).
2021 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/gs-20-521). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Randolph GW, Duh QY, Heller KS, et al. The prognostic significance of nodal metastases from papillary thyroid carcinoma can be stratified based on the size and number of metastatic lymph nodes, as well as the presence of extranodal extension. Thyroid 2012;22:1144-52. 10.1089/thy.2012.0043 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
