Roles of specific drug therapies for severe pulmonary arterial hypertension in palliative care: a case report
- PMID: 33634247
- PMCID: PMC7882262
- DOI: 10.21037/acr-20-108
Roles of specific drug therapies for severe pulmonary arterial hypertension in palliative care: a case report
Abstract
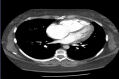
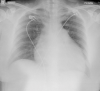
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening illness. The elevated pulmonary arterial blood pressure will lead to right heart failure and even cardiopulmonary collapse if it is severe. Apart from general supportive measures, pulmonary hypertension-specific therapies (PHST) are available to slow down disease progression, but they are not curative. According to previous studies, many patients with severe PAH often had significant physical symptoms and psychological distress for both themselves and their families at the end of life. Moreover, they would have repeated admissions due to physical deterioration and decline in functioning associated with worsening in cardiac function. Some of these patients might suffer from unnecessary aggressive interventions and resuscitation because of lack of advance care planning discussion. As such, Palliative Care (PC) would be an important element as part of the overall management. Hereby, we reported a patient with severe PAH and schizoaffective disorder achieved good outcome from the use of combination PHST and PC input. Her physical and psychosocial needs could be addressed well by PC team. This case report showed the collaborative work between PC and parent teams. While parent team was able to manage the medical conditions related to PAH, however the physical and psychosocial needs should be addressed by PC team. More importantly, the PC team has essential roles of providing advance care planning discussions with the patient and help to reduce unnecessary interventions. Furthermore, PC would coordinate the community service to support her while staying at home. Roles of PHST will also be discussed in this case. Clinicians must take into account possible hemodynamic effects of any palliative intervention for PAH.
Keywords: Pulmonary hypertension; palliative care (PC); selexipag.
2021 AME Case Reports. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/acr-20-108). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Symptom burden, quality of life, and attitudes toward palliative care in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: results from a cross-sectional patient survey.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012 Oct;31(10):1102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2012.08.010. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22975100
-
Physician attitudes toward palliative care for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: results of a cross-sectional survey.Pulm Circ. 2014 Sep;4(3):504-10. doi: 10.1086/677365. Pulm Circ. 2014. PMID: 25621164 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Palliative Medicine Review of the Disease, Its Therapies, and Drug Interactions.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2020 Apr;59(4):932-943. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.11.023. Epub 2019 Dec 2. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2020. PMID: 31805363 Review.
-
Palliative care for people living with heart failure: European Association for Palliative Care Task Force expert position statement.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Jan 1;116(1):12-27. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz200. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31386104 Review.
-
Palliative care for people living with cardiac disease.Kardiol Pol. 2020 Apr 24;78(4):364-373. doi: 10.33963/KP.15276. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Kardiol Pol. 2020. PMID: 32336071
References
-
- Task Force for Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of European Society of Cardiology (ESC) European Respiratory Society (ERS) ; International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2009;34:1219-63. 10.1183/09031936.00139009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials