Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and diabetic retinopathy: insights into preservation of sight and looking beyond
- PMID: 33634250
- PMCID: PMC7901818
- DOI: 10.1097/XCE.0000000000000209
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and diabetic retinopathy: insights into preservation of sight and looking beyond
Abstract
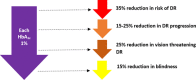
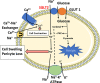
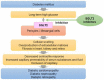
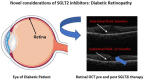
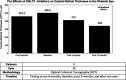
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i) were initially developed as therapeutic options for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Recently, randomized clinical trials have investigated their effects in cardiorenal protection through major adverse cardiovascular event reduction and reductions in diabetic nephropathy. While multiple mechanisms are proposed for this protection, microvascular protection is the primary component of their efficacy. While not primarily emphasized in clinical trials, evidence in other studies suggests that SGLT2i may confer retinoprotective effects via some of the same mechanisms in the aforementioned cardiorenal trials. Diabetic patients are susceptible to vision loss with chronic hyperglycemia promoting inflammation, edema, and retinal pathological changes. Targeting these pathways via SGLT2i may represent opportunities for providers to decrease retinopathy in high-risk T2DM patients, reduce disease progression, and lower drug burden in diabetic retinopathy patients. Further comprehensive clinical trials investigating these associations are needed to establish the potential retinoprotective effects of SGLT2i.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic; diabetology; microvascular; ophthalmology; retina; retinopathy; sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors; translational biology; vision loss.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes and Cardiorenal Complications: A Clinical Review of Existing Therapies and Novel Combinations, Focusing on SGLT2 Inhibitors.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023;19(8):e160822207546. doi: 10.2174/1573399819666220816145907. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023. PMID: 35975848 Review.
-
Cardiorenal protection with SGLT2: Lessons from the cardiovascular outcome trials.J Diabetes. 2020 Apr;12(4):279-293. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13007. Epub 2019 Dec 11. J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 31688975 Review.
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors increase Klotho in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A clinical and experimental study.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Oct;154:113677. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113677. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36942605
-
Cardiorenal Protections of SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023;19(8):e221222212126. doi: 10.2174/1573399819666221222160035. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023. PMID: 36567296 Review.
-
The association between the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor and the risk of diabetic retinopathy and other eye disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Jul;15(7):877-886. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2102973. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35839519
Cited by
-
Commentary: Oral management of diabetic retinopathy.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;69(11):3327-3328. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2088_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34708797 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on diabetic macular edema and the need for intravitreal injection.Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 18;18(7):1326-1332. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.07.16. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40688778 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: a real-world data study from a global federated database.Diabetologia. 2024 Jul;67(7):1271-1282. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06132-5. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38584180 Free PMC article.
-
Dapagliflozin protects neural and vascular dysfunction of the retina in diabetes.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022 May;10(3):e002801. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2022-002801. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022. PMID: 35577387 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin and the Risk of Retinopathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan 1;143(1):62-71. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.5219. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39636645
References
-
- Cox DJ, Kiernan BD, Schroeder DB, Cowley M. Psychosocial sequelae of visual loss in diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 1998; 24:481–484. - PubMed
-
- Fenwick EK, Pesudovs K, Khadka J, Dirani M, Rees G, Wong TY, Lamoureux EL. The impact of diabetic retinopathy on quality of life: qualitative findings from an item bank development project. Qual Life Res. 2012; 21:1771–1782. - PubMed
-
- Kuniss N, Freyer M, Müller N, Kielstein V, Müller UA. Expectations and fear of diabetes-related long-term complications in people with type 2 diabetes at primary care level. Acta Diabetol. 2019; 56:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
