A cross-sectional study of screening for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) at the pediatric emergency department in Vilnius during the first wave of the pandemic
- PMID: 33634336
- PMCID: PMC7906570
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-021-03999-z
A cross-sectional study of screening for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) at the pediatric emergency department in Vilnius during the first wave of the pandemic
Abstract
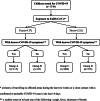
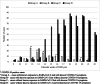
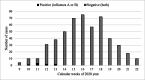
Screening for COVID-19 is based on clinical and epidemiological factors. Children infected with SARS-CoV-2 may have a few or many non-specific symptoms or may be asymptomatic. The aim of this study was to analyze clinical features and exposure to SARS-CoV-2 characteristics of children screened for COVID-19 at the pediatric emergency department in Vilnius during the first 3 months (March-May) of the COVID-19 pandemic in Lithuania. SARS-CoV-2 PCR was positive for 0.6% (8/1348) of all screened children and for 0.9% (7/811) of symptomatic patients, more among children with fever and cough (2.6%, 4/154). There were also COVID-19 cases among children without cough but with other respiratory symptoms (0.5%, 2/409) or gastrointestinal symptoms (1.2%, 3/257). Only one child with positive SARS-CoV-2 did not meet COVID-19 clinical criteria-he presented with vomiting and dehydration only. All COVID-19 cases (n = 8) had a contact with a confirmed COVID-19 family member. There were no COVID-19 cases among children without known exposure to SARS-CoV-2 or among asymptomatic children.Conclusion: Screening for COVID-19 in children is exceptionally challenging due to the diverse and non-specific symptoms of infection they present. Testing strategies should not only focus on the typical COVID-19 symptoms of fever or cough, but also include other symptoms, especially gastrointestinal symptoms, which are also important. The greatest attention should be paid to known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, especially in family clusters. Screening of asymptomatic children with no known exposure should be weighed for medical necessity and cost-effectiveness. What is Known: • Diagnosis of COVID-19 in children is challenging because the disease does not always manifest with typical symptoms. What is New: • Children in our study who did not have symptoms of acute infection and contact with another person infected with COVID-19 were not diagnosed with COVID-19, so the benefit of PCR testing is questionable. Such testing may only be useful for infection control purposes, and to limit intra-hospital transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Children; PCR; Pediatric emergency department; Screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Archived: WHO timeline - COVID-19. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-04-2020-who-timeline%2D%2D-covid-19. Accessed September 5, 2020
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (2020) COVID-19 situation update worldwide, as of 5 September 2020. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases. Accessed September 5, 2020
-
- Registrų centras (2020) Koronaviruso (COVID-19) Lietuvoje statistika. https://registrucentras.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/be.... Accessed May 31, 2020
-
- Götzinger F, Santiago-García B, Noguera-Julián A, Lanaspa M, Lancella L, Calò Carducci FI, Gabrovska N, Velizarova S, Prunk P, Osterman V, Krivec U, Lo Vecchio A, Shingadia D, Soriano-Arandes A, Melendo S, Lanari M, Pierantoni L, Wagner N, L'Huillier AG, Heininger U, Ritz N, Bandi S, Krajcar N, Roglić S, Santos M, Christiaens C, Creuven M, Buonsenso D, Welch SB, Bogyi M, Brinkmann F, Tebruegge M, Pfefferle J, Zacharasiewicz A, Berger A, Berger R, Strenger V, Kohlfürst DS, Zschocke A, Bernar B, Simma B, Haberlandt E, Thir C, Biebl A, vanden Driessche K, Boiy T, van Brusselen D, Bael A, Debulpaep S, Schelstraete P, Pavic I, Nygaard U, Glenthoej JP, Heilmann Jensen L, Lind I, Tistsenko M, Uustalu Ü, Buchtala L, Thee S, Kobbe R, Rau C, Schwerk N, Barker M, Tsolia M, Eleftheriou I, Gavin P, Kozdoba O, Zsigmond B, Valentini P, Ivaškeviciene I, Ivaškevicius R, Vilc V, Schölvinck E, Rojahn A, Smyrnaios A, Klingenberg C, Carvalho I, Ribeiro A, Starshinova A, Solovic I, Falcón L, Neth O, Minguell L, Bustillo M, Gutiérrez-Sánchez AM, Guarch Ibáñez B, Ripoll F, Soto B, Kötz K, Zimmermann P, Schmid H, Zucol F, Niederer A, Buettcher M, Cetin BS, Bilogortseva O, Chechenyeva V, Demirjian A, Shackley F, McFetridge L, Speirs L, Doherty C, Jones L, McMaster P, Murray C, Child F, Beuvink Y, Makwana N, Whittaker E, Williams A, Fidler K, Bernatoniene J, Song R, Oliver Z, Riordan A. COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: a multinational, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020;4:653–661. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30177-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

