Blood Biomarker Panels for the Early Prediction of Stroke-Associated Complications
- PMID: 33634708
- PMCID: PMC8174272
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018946
Blood Biomarker Panels for the Early Prediction of Stroke-Associated Complications
Abstract
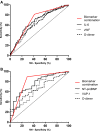
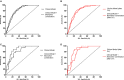
Background Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) and respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are potentially life-threatening complications in patients experiencing stroke during hospitalization. We aimed to test whether blood biomarker panels might predict these complications early after admission. Methods and Results Nine hundred thirty-eight patients experiencing ischemic stroke were prospectively recruited in the Stroke-Chip study. Post-stroke complications during hospitalization were retrospectively evaluated. Blood samples were drawn within 6 hours after stroke onset, and 14 biomarkers were analyzed by immunoassays. Biomarker values were normalized using log-transformation and Z score. PanelomiX algorithm was used to select panels with the best accuracy for predicting ADHF and RTI. Logistic regression models were constructed with the clinical variables and the biomarker panels. The additional predictive value of the panels compared with the clinical model alone was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic curves. An internal validation through a 10-fold cross-validation with 3 repeats was performed. ADHF and RTI occurred in 19 (2%) and 86 (9.1%) cases, respectively. Three-biomarker panels were developed as predictors: vascular adhesion protein-1 >5.67, NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide) >4.98 and d-dimer >5.38 (sensitivity, 89.5%; specificity, 71.7%) for ADHF; and interleukin-6 >3.97, von Willebrand factor >3.67, and d-dimer >4.58 (sensitivity, 82.6%; specificity, 59.8%) for RTI. Both panels independently predicted stroke complications (panel for ADHF: odds ratio [OR] [95% CI], 10.1 [3-52.2]; panel for RTI: OR, 3.73 [1.95-7.14]) after adjustment by clinical confounders. The addition of the panel to clinical predictors significantly improved areas under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic curves in both cases. Conclusions Blood biomarkers could be useful for the early prediction of ADHF and RTI. Future studies should assess the usefulness of these panels in front of patients experiencing stroke with respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea.
Keywords: ADHF; biomarkers; stroke; stroke‐associated infection.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

