ST-elevation versus non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction after combined use of statin with renin-angiotensin system inhibitor: Data from the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry
- PMID: 33634844
- PMCID: PMC9273248
- DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2021.0007
ST-elevation versus non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction after combined use of statin with renin-angiotensin system inhibitor: Data from the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry
Abstract
Background: Limited data are available comparing the combined effects of statins and renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASI) between patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and those with non-STEMI (NSTEMI). We compared the effects of statins combined with RASI in STEMI and NSTEMI patients after stent implantation during a long-term follow-up period.
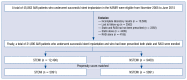
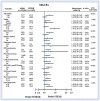
Methods: A total of 21,890 acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients who underwent successful stent implantation and who received statins with RASI were enrolled. They were separated into the STEMI group (n = 12,490) and the NSTEMI group (n = 9400). The major clinical endpoint was the occurrence of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) defined as all-cause death, recurrent myocardial infarction (Re-MI), and any repeat revascularization.
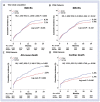
Results: Two propensity score-matched (PSM) groups (5891 pairs, n = 11782, C-statistic = 0.821) were generated. Even though the cumulative incidences of MACE, re-MI, total repeat revascularization were similar between the two groups, the cumulative incidences of all-cause death (hazard ratio [HR] 1.407; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.106-1.790; p = 0.005) and cardiac death (HR 1.311; 95% CI 1.983-1.749; p = 0.046) were significantly higher in the NSTEMI group.
Conclusions: In this study, statin with RASI combination therapy was more beneficial to the STEMI patients than to the NSTEMI patients in reducing all-cause death and cardiac death.
Keywords: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; renin–angiotensin system; statin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on long-term clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with successful percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents: Comparison between STEMI and NSTEMI.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Jan;280:166-173. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.11.030. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 30529829
-
Monotherapy versus combination therapy of statin and renin-angiotensin system inhibitor in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Cardiol J. 2022;29(1):93-104. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0035. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Cardiol J. 2022. PMID: 32207841 Free PMC article.
-
Different Statin Effects of ST-elevation Versus Non-ST-Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction After Stent Implantation.Am J Med Sci. 2020 Mar;359(3):156-167. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2019.12.004. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Am J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32089157
-
Contemporary NSTEMI management: the role of the hospitalist.Hosp Pract (1995). 2020 Feb;48(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/21548331.2020.1701329. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Hosp Pract (1995). 2020. PMID: 31815570 Review.
-
Secondary electrocardiographic stratification of NSTEMI to identify an acutely occluded culprit artery.Physiol Meas. 2023 Jul 17;44(7). doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/acddc8. Physiol Meas. 2023. PMID: 37307848 Review.
References
-
- Larsen AI, Tomey MI, Mehran R, et al. Comparison of outcomes in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction discharged on versus not on statin therapy (from the Harmonizing Outcomes With Revascularization and Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction Trial) Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(8):1273–1279. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.01.401. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR) Eur Heart J. 2016;37(29):2315–2381. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2018;39(2):119–177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

