Development of an ICF Core Set for adults with cerebral palsy: capturing their perspective on functioning
- PMID: 33634853
- PMCID: PMC8248089
- DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.14841
Development of an ICF Core Set for adults with cerebral palsy: capturing their perspective on functioning
Abstract
Aim: To examine the most relevant aspects of functioning of adults with cerebral palsy (CP) from their perspective, in order to develop an International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Core Set for adults with CP.
Method: We conducted six focus group discussions with adults with CP without intellectual disability and seven interviews with adults with CP with intellectual disability and caregivers, addressing all ICF components. Meaningful concepts were identified from verbatim transcripts and linked to ICF categories by two independent researchers.
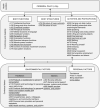
Results: In total, 31 adults with CP without intellectual disability (mean [SD] age 46y 1mo [14y 1mo]; 20 females, 11 males; Gross Motor Function Classification System [GMFCS] levels I-IV) and seven adults with CP and intellectual disability (mean [SD] age 25y 8mo [6y 8mo]; four females, three males; GMFCS levels III-V) participated. We identified 132 unique second-level categories: 47 body functions, seven body structures, 43 activities and participation, and 35 environmental factors. The most frequently mentioned categories were emotional function, pain, muscle tone function, support of family, products and technology, and health services.
Interpretation: Adults with CP experienced problems in a broad range of body functions and activities and indicated the importance of environmental factors for functioning. The identified categories will be added to the list of candidate items to reach consensus on an ICF Core Set for adults with CP. What this paper adds Including the lived experience is crucial for fully understanding functioning of adults with cerebral palsy (CP). Adults with CP perceive environmental factors as essential elements for everyday functioning. Adults with intellectual disability should be considered as a group with specific problems.
Objetivo: Examinar los aspectos más relevantes del funcionamiento de los adultos con parálisis cerebral (PC) desde su perspectiva, con el fin de desarrollar un Conjunto Basico de la Clasificación Internacional del Funcionamiento, de la Discapacidad y de la Salud (CIF) para adultos con PC.
Método: Realizamos seis grupos focales con adultos con PC sin discapacidad intelectual y siete entrevistas con adultos con PC con discapacidad intelectual y cuidadores, abordando todos los componentes de la CIF. Se identificaron conceptos significativos a partir de transcripciones textuales y se vincularon a las categorías de la CIF por dos investigadores independientes.
Resultados: En total, 31 adultos con PC sin discapacidad intelectual (edad media [DE] 46 años 1 mes [14 años 1 mes]; 20 mujeres, 11 hombres; sistema de clasificación de la función motora gruesa [GMFCS] niveles I‐IV) y siete adultos con PC con discapacidad intelectual participaron (media [DE] edad 25 años 8 meses [6 años 8 meses]; cuatro mujeres, tres hombres; niveles de GMFCS III‐V). Identificamos 132 categorías únicas de segundo nivel: 47 funciones corporales, siete estructuras corporales, 43 actividades y participación y 35 factores ambientales. Las categorías mencionadas con mayor frecuencia fueron función emocional, dolor, función del tono muscular, apoyo a la familia, productos y tecnología y servicios de salud.
Interpretación: Los adultos con PC experimentaron problemas en una amplia gama de funciones y actividades corporales e indicaron la importancia de los factores ambientales para su funcionamiento. Las categorías identificadas se agregarán a la lista de elementos candidatos para llegar a un consenso sobre un conjunto básico de la CIF para adultos con PC.
Objetivo: Descrever os aspectos mais relevantes do funcionamento para adultos com paralisia cerebral (PC) a partir de sua perspectiva, a fim de desenvolver um Conjunto Principal de itens da Classificação Internacional de Incapacidade, Funcionalidade e Saúde (CIF) para adultos com PC.
Método: Conduzimos seis discussões em grupos focais com adultos com PC sem deficiência intelectual e sete entrevistas com adultos com PC e deficiência intelectual e seus cuidadores, abordando todos os componentes da CIF. Conceitos significativos foram identificados a partir das transcrições das falas e ligados a categorias da CIF por dois pesquisadores independentes.
Resultados: No total, 31 adultos com PC sem deficiência intelectual (média [DP] de idade 46a 1m [14a 1m]; 20 do sexo masculino, 11 do sexo feminino; Sistema de Classificação da Função Motora Grossa [GMFCS] níveis I–IV) e sete adultos com PC e deficiência intelectual (média [DP] de idade 25a 8m [6a 8m]; quatro do sexo masculino, três do sexo feminino ; níveis GMFCS III–V) participaram. Identificamos 132 categorias de segundo nível únicas: 47 em funções do corpo, sete em estruturas do corpo, 43 em atividades e participação, e 35 fatores ambientais. As categorias mais frequentemente mencionadas foram função emocional, dor, função do tônus muscular, suporte da família, produtos e tecnologia, e serviços de saúde.
Interpretação: Adultos com PC experienciam problemas um uma ampla variedade de funções do corpo e atividades e participação, e indicaram a importância de fatores ambientais para o funcionamento. As categorias identificadas serão adicionadas à lista de itens candidatos a obter consenso em um conjunto principal de itens da CIF para adultos com PC.
© 2021 The Authors. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Mac Keith Press.
Figures
Comment in
-
Transitional milestones and developmental challenges for adults with cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2021 Jul;63(7):766. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14894. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33834496 No abstract available.
References
-
- Oskoui M, Coutinho F, Dykeman J, Jette N, Pringsheim T. An update on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol 2013; 55: 509–19. - PubMed
-
- Sellier E, Platt MJ, Andersen GL, et al. Decreasing prevalence in cerebral palsy: a multi‐site European population‐based study, 1980 to 2003. Dev Med Child Neurol 2016; 58: 85–92. - PubMed
-
- Brooks JC, Strauss DJ, Shavelle RM, Tran LM, Rosenbloom L, Wu YW. Recent trends in cerebral palsy survival. Part II: individual survival prognosis. Dev Med Child Neurol 2014; 56: 1065–71. - PubMed
-
- van Gorp M, Roebroeck ME, van Eck M, et al. Childhood factors predict participation of young adults with cerebral palsy in domestic life and interpersonal relationships: a prospective cohort study. Disabil Rehabil 2020; 42: 3162–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

