Membrane engineering of cell membrane biomimetic nanoparticles for nanoscale therapeutics
- PMID: 33635002
- PMCID: PMC7819108
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.292
Membrane engineering of cell membrane biomimetic nanoparticles for nanoscale therapeutics
Abstract
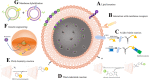
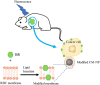
In recent years, cell membrane camouflaging technology has emerged as an important strategy of nanomedicine, and the modification on the membranes is also a promising approach to enhance the properties of the nanoparticles, such as cancer targeting, immune evasion, and phototherapy sensitivity. Indeed, diversified approaches have been exploited to re-engineer the membranes of nanoparticles in several studies. In this review, first we discuss direct modification strategy of cell membrane camouflaged nanoparticles (CM-NP) via noncovalent, covalent, and enzyme-involved methods. Second, we explore how the membranes of CM-NPs can be re-engineered at the cellular level using strategies such as genetic engineering and membranes fusion. Due to the innate biological properties and excellent biocompatibility, the functionalized cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles have been widely applied in the fields of drug delivery, imaging, detoxification, detection, and photoactivatable therapy.
Keywords: cell membrane camouflaged nanoparticles; membrane engineering; nanoscale therapeutics.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Jiang T, Zhang B, Zhang L, et al. Biomimetic nanoparticles delivered hedgehog pathway inhibitor to modify tumour microenvironment and improved chemotherapy for pancreatic carcinoma. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):1088‐1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
