Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme 2 and Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19: An Update
- PMID: 33635533
- PMCID: PMC7908946
- DOI: 10.1007/s40292-021-00439-9
Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme 2 and Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19: An Update
Abstract
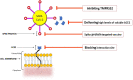
Ever since its outbreak, Corona Virus Disease 2019(COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 has affected more than 26 million individuals in more than 200 countries. Although the mortality rate of COVID-19 is low, but several clinical studies showed, patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) or other major complication at high risk of COVID-19 and reported more severe disease and increased fatality. The angiotensin-converting-enzyme 2 (ACE2), a component of renin-angiotensin-system (RAS); acts on ACE/Ang-II/AT1recptor axis, and regulates pathological processes like hypertension, cardiac dysfunction, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) etc. The progression of T2DM and hypertension show decreased expression and activity of ACE2. There are several treatment strategies for controlling diabetes, hypertension, etc; like ACE2 gene therapies, endogenous ACE2 activators, human recombinant ACE2 (hrACE2), Angiotensin-II receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors (ACEi) medications. ACE2, the receptors for SARS-CoV2, facilitates virus entry inside host cell. Clinicians are using two classes of medications for the treatment of COVID-19; one targets the SARS-CoV-2-ACE2 interaction, while other targets human immune system. The aim of this review is to discuss the role of ACE2 in diabetes and in COVID-19 and to provide an analysis of data proposing harm and benefit of RAS inhibitor treatment in COVID-19 infection as well as showing no association whatsoever. This review also highlights some candidate vaccines which are undergoing clinical trials.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19; Comorbidity; Diabetes; RAS inhibitors; Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commentary to Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme 2 and Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19: An Update.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021 May;28(3):251-252. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00446-w. Epub 2021 Apr 1. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021. PMID: 33792849 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese Center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

