Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging for chronic liver disease
- PMID: 33635729
- PMCID: PMC8506189
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20201377
Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging for chronic liver disease
Abstract
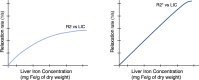
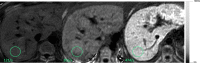
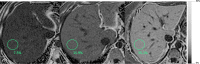
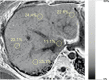
Chronic liver disease (CLD) has rapidly increased in prevalence over the past two decades, resulting in significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. Historically, the clinical gold standard for diagnosis, assessment of severity, and longitudinal monitoring of CLD has been liver biopsy with histological analysis, but this approach has limitations that may make it suboptimal for clinical and research settings. Magnetic resonance (MR)-based biomarkers can overcome the limitations by allowing accurate, precise, and quantitative assessment of key components of CLD without the risk of invasive procedures. This review briefly describes the limitations associated with liver biopsy and the need for non-invasive biomarkers. It then discusses the current state-of-the-art for MRI-based biomarkers of liver iron, fat, and fibrosis, and inflammation.
Figures
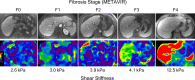
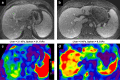
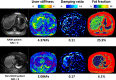
Similar articles
-
Multiparametric MR assessment of liver fat, iron, and fibrosis: a concise overview of the liver "Triple Screen".Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023 Jun;48(6):2060-2073. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-03887-0. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023. PMID: 37041393 Review.
-
Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis: exploring the opportunity for a low-cost approach using the Genoa Line Quantification.Panminerva Med. 2018 Sep;60(3):77-79. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.18.03444-4. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Panminerva Med. 2018. PMID: 29546739 No abstract available.
-
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Assessing Fat, Iron, and Fibrosis in Chronic Liver Disease.Gut Liver. 2025 Jan 15;19(1):31-42. doi: 10.5009/gnl240302. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Gut Liver. 2025. PMID: 39774121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Liver Fibrosis, Fat, and Iron.Radiol Clin North Am. 2022 Sep;60(5):705-716. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2022.04.003. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Radiol Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 35989039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic Resonance Elastography of Liver: Current Update.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 Oct;27(5):319-333. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0000000000000177. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 30289828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiology of fibrosis part II: abdominal organs.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 2;22(1):610. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05346-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38956593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Future Is Beyond Bright: The Evolving Role of Quantitative US for Fatty Liver Disease.Radiology. 2023 Nov;309(2):e223146. doi: 10.1148/radiol.223146. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 37934095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-Specific Contribution of Cardiometabolic Index in Predicting Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: Insights from a General Population.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Nov 30;16:3871-3883. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S437413. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 38054037 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability-encouraging self-supervised learning reconstruction for quantitative MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Aug;94(2):797-809. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30478. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40014485 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiometabolic index: A new predictor for metabolic associated fatty liver disease in Chinese adults.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 16;13:1004855. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1004855. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36187093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tan Y-W, Zhou X-B, Ye Y, He C, Ge G-H. Diagnostic value of FIB-4, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index and liver stiffness measurement in hepatitis B virus-infected patients with persistently normal alanine aminotransferase. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23: 5746: 5746. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5746 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

