Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Aging and Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33636114
- PMCID: PMC8072031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.01.019
Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Aging and Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
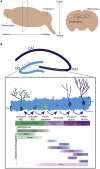
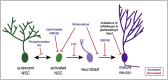
Cognitive deficits associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) severely impact daily life for the millions of affected individuals. Progressive memory impairment in AD patients is associated with degeneration of the hippocampus. The dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, a region critical for learning and memory functions, is a site of adult neurogenesis in mammals. Recent evidence in humans indicates that hippocampal neurogenesis likely persists throughout life, but declines with age and is strikingly impaired in AD. Our understanding of how neurogenesis supports learning and memory in healthy adults is only beginning to emerge. The extent to which decreased neurogenesis contributes to cognitive decline in aging and AD remains poorly understood. However, studies in rodent models of AD and other neurodegenerative diseases raise the possibility that targeting neurogenesis may ameliorate cognitive dysfunction in AD. Here, we review recent progress in understanding how adult neurogenesis is impacted in the context of aging and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; adult neurogenesis; aging; cognitive decline; neural stem cell.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):7369-7383. doi: 10.1002/alz.14179. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39166771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and its impairment in Alzheimer's disease.Zool Res. 2022 May 18;43(3):481-496. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2021.479. Zool Res. 2022. PMID: 35503338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Feb;84:101828. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101828. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36549424 Review.
-
proNGF Involvement in the Adult Neurogenesis Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 4;22(19):10744. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910744. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639085 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease and Potential Therapeutic Approaches.Cells. 2022 Jan 15;11(2):286. doi: 10.3390/cells11020286. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053402 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can exercise benefits be harnessed with drugs? A new way to combat neurodegenerative diseases by boosting neurogenesis.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Jul 25;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00428-7. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39049102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in neural progenitors controls KDM5A to influence neuronal differentiation.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Sep;54(9):1461-1471. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00841-w. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36056186 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise mimetics: a novel strategy to combat neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Feb 2;21(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03031-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38308368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related differences in hippocampal subfield volumes across the human lifespan: A meta-analysis.Hippocampus. 2023 Dec;33(12):1292-1315. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23582. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 37881160 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-level genomic convergence of secondary aquatic adaptation in marine mammals.Innovation (Camb). 2025 Jan 3;6(3):100798. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2025.100798. eCollection 2025 Mar 3. Innovation (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40098664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aimone J.B., Wiles J., Gage F.H. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat. Neurosci. 2006;9:723–727. - PubMed
-
- Altman J., Das G.D. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
-
- Ambrogini P., Lattanzi D., Ciuffoli S., Agostini D., Bertini L., Stocchi V., Santi S., Cuppini R. Morpho-functional characterization of neuronal cells at different stages of maturation in granule cell layer of adult rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 2004;1017:21–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

