COVID-19-related arrhythmias and the possible effects of ranolazine
- PMID: 33636586
- PMCID: PMC7890340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2021.110545
COVID-19-related arrhythmias and the possible effects of ranolazine
Abstract
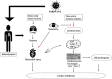
The COVID-19 pandemic has become a burden to the global healthcare community. Despite the severity of the complications associated with COVID-19, no antiviral agent is yet available for the treatment of this disease. Several studies have reported arrhythmias as one of the numerous manifestations associated with COVID-19 infection. Clinicians use different therapeutic agents in the management of COVID-19 patients with arrhythmias, apart from ranolazine; however, some of these drugs are administered with caution because of their significant side effects. In this study, we reviewed the potential antiarrhythmic effects of ranolazine in the management of cardiac arrhythmias associated with COVID-19. Ranolazine is a second-line drug approved for the treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris. Previous studies have shown that ranolazine produces its beneficial cardiac effects without any significant impact on the body's hemodynamics; hence, blood pressure is not altered. Due to its reduced side effects, ranolazine may be more effective than other drugs in producing the desired relief from COVID-19 related arrhythmias, since it produces its antiarrhythmic effect by modulating sodium, potassium and calcium channels, and suppressing cytokine expression.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; COVID-19; Cytokine; Ranolazine; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ranolazine in Cardiac Arrhythmia.Clin Cardiol. 2016 Mar;39(3):170-8. doi: 10.1002/clc.22476. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Clin Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26459200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ranolazine and its Antiarrhythmic Actions.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2015;13(1):31-9. doi: 10.2174/187152571301150730113903. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26245658 Review.
-
Ranolazine: Electrophysiologic Effect, Efficacy, and Safety in Patients with Cardiac Arrhythmias.Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2016 Jun;8(2):467-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2016.02.011. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2016. PMID: 27261835 Review.
-
Inhibition of Late Sodium Current as an Innovative Antiarrhythmic Strategy.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017 Jun;14(3):179-186. doi: 10.1007/s11897-017-0333-0. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017. PMID: 28455610 Review.
-
The antiarrhythmic effects of ranolazine.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2009;10 Suppl 1:S38-45. doi: 10.3909/ricm10S10006. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2009. PMID: 19898287 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug repurposing of argatroban, glimepiride and ranolazine shows anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity via diverse mechanisms.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 10;11(3):e41894. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41894. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39968139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- COVID-19 Map In. Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center [Online]. Available: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. [Accessed 2 January 2020].
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

